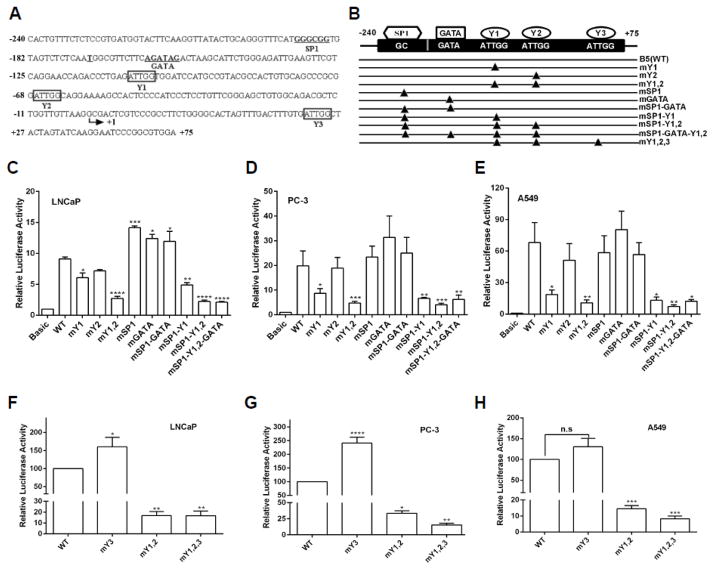
Fig. 2.
The two CCAAT boxes are critical for the proximal promoter activity of PRMT5. (A) Sequences of the proximal promoter region from −240 to +75 with predicted cis-regulatory elements. The transcription start site was indicated by arrow. Y1, Y2, or Y3 indicates the first, second or third NF-Y binding site. (B) Illustration of a series of B5-based luciferase reporter gene constructs. Triangle indicates the corresponding cis-regulatory element was mutated. (C–E) CCAAT boxes are critical for luciferase activity driven by the PRMT5 promoter. The luciferase activity of the indicated reporter gene constructs in B was determined in the indicated cancer cell lines. (F–H) The third NF-Y binding site has little effect on the PRMT5 promoter activity. The indicated luciferase reporter gene was co-transfected with pRL-TK into LNCaP (F), PC-3 (G) and A549 (H) cells for 24 hours, and the relative luciferase activity was determined. Results in C-H were from at least three independent experiments, and were normalized to the vector control and are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance (*, p<0.05, **, p<0.01, ***, p<0.001 and ****, p<0.0001) was determined when compared with WT (wild-type) by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test.