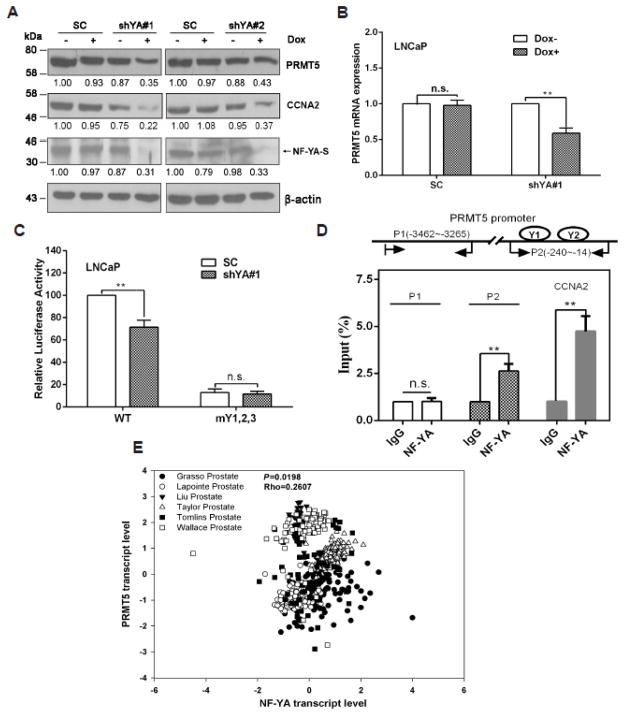
Fig. 3.
NF-Y is essential for PRMT5 expression in LNCaP cells. (A) NF-YA knockdown inhibits PRMT5 expression. Doxycycline (Dox) was added at 1 μg/ml for 96 hours to induce NF-YA knockdown in ShYA#1 and shYA#2 stable cell lines, and total cell lysate was used for immunoblotting analysis of PRMT5, shorter isoform of NF-YA (NF-YA-S), CCNA2 and β-actin. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments, and the numbers indicate relative fold changes analyzed by Image J. (B) Knockdown of NF-YA inhibits PRMT5 mRNA expression. shRNA expression was induced by Dox for 72 hours, and qRT-PCR was performed to determine the mRNA level of PRMT5. Results are mean ± SEM from 4 independent experiments, and student’s t test was used for statistical analysis (**, p<0.01). (C) Knockdown of NF-YA decreases the PRMT5 proximal promoter activity. One μg of plasmids encoding SC or shYA1# (with Dox induction) was co-transfected with 0.5 μg of the B5 reporter gene plasmid (WT) or the mutant reporter gene (mY1,2,3), along with 100 ng of pRL-TK into LNCaP for 48 hours, and Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assays were performed and analyzed. Luciferase activities are presented as percentage from at least three independent experiments. **, p<0.01. (D) NF-YA binds to the two inverted CCAAT boxes. Shown (top) is a schematic of the two regions (P1 and P2) in the PRMT5 promoter for ChIP analysis. Results (bottom) are mean ± SEM from four independent experiments (**, p<0.01). The binding of NF-YA to the CCNA2 promoter was used as a positive control. (E) The transcript level of NF-YA positively correlates with the transcript level of PRMT5 in prostate cancer. Data shown are a meta-analysis from six independent studies deposited in Oncomine database.