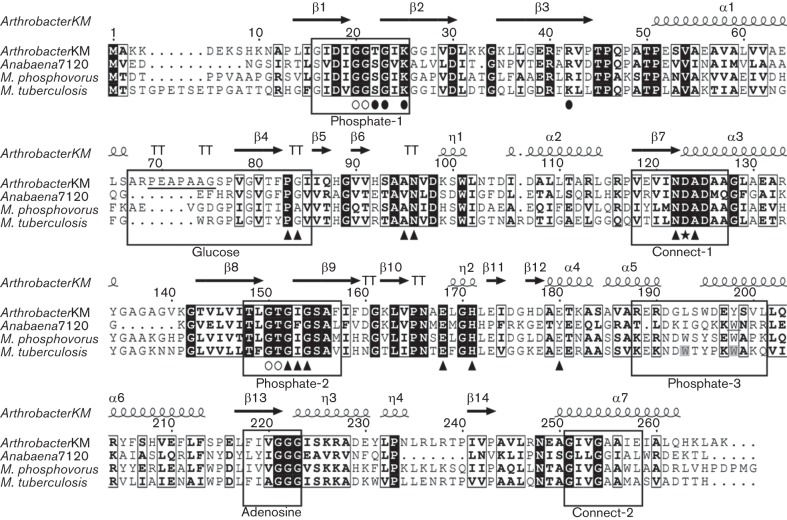
Fig. 1.
Primary structural alignments of different PPGKs. Aligned primary structures from Arthrobacter sp. strain KM, Microlunatus phosphovorus (Tanaka et al., 2003), Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Hsieh et al., 1993; Phillips et al., 1999) and Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Strictly conserved residues are shaded in black; similar residues are framed in black. Putative structural and functional domains are enclosed in boxes. Secondary structural elements [e.g. α helices, β sheets, turn-turns (TT)] of the polyP/ATP-glucomannokinase from Arthrobacter sp. strain KM are depicted above the alignment. Residues associated with β-d-glucose binding are marked with filled triangles. The heptapeptide is underlined. The catalytic aspartate (D) is highlighted with a star. Residues involved in the binding of both phosphate molecules used as ligands (open, phosphate A; filled, phosphate B) are marked with ovals (Mukai et al., 2004).