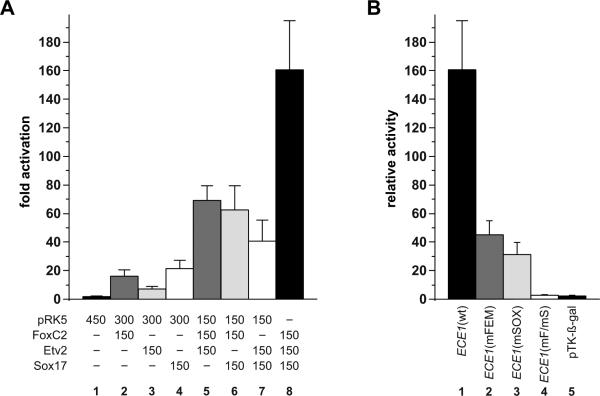
FIG. 6.
Synergistic activation of the ECE1 enhancer by combinatorial expression of Sox17, FoxC2, and Etv2 requires binding to the cognate binding site for each factor. (A) Cos-1 cells were transfected with the wild type ECE1-TK-β-gal reporter plasmid and various combinations of pRK5 expression plasmids for FoxC2, Etv2, and Sox17 and were assayed for E-galactosidase activity. The amount (ng) of each transfected expression plasmid is indicated. Data are expressed as the mean fold activation of reporter co-transfected with parental expression plasmid only plus SEM for 3 independent transfections and analyses. (B) Cos-1 cells were transfected with expression plasmids for FoxC2, Etv2, and Sox17 (150 ng each plasmid) and various ECE1-TK-β-gal reporter plasmids, including the wild type (wt, lane 1), mutated FOX:ETS motif (mFEM, lane 2), mutated SOX site (mSOX, lane 3), both FOX:ETS motif and SOX sites mutated (mF/mS, lane 4), and the parental pTK-E-gal reporter lacking ECE1 elements (lane 5). Maximal activation by the three transactivators was only observed when both cis-acting elements were intact (lane 1). Data are expressed as the mean relative β-galactosidase activity plus SEM for 3 independent transfections and analyses.