Figure 6. TJ dynamic behavior and barrier function are regulated through occludin S408 phosphorylation.
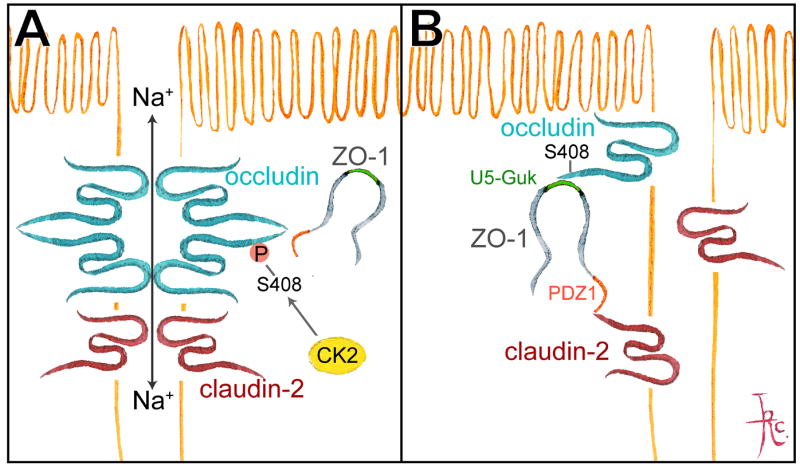
A. CK2-mediated occludin S408 phosphorylation promotes assembly of occludin dimers that are highly mobile within the tight junction. Claudin-2 forms complexes with claudin-2 on adjacent cells to create paracellular cation pores. B. CK2 inhibition and occludin S408 dephosphorylation promotes occludin binding to ZO-1 which, in turn, binds to claudin-2. This increases claudin-2 mobility, which disrupts claudin-2 interactions and cation pores. C. Stable association of ZO-1 with occludin (after CK2 inhibition) converts part of ZO-1 mobility to a diffusive process, with fluorescence recovery beginning at the edges of the bleached region. From Raleigh et al. J Cell Biol. 2011.
