Fig 1.
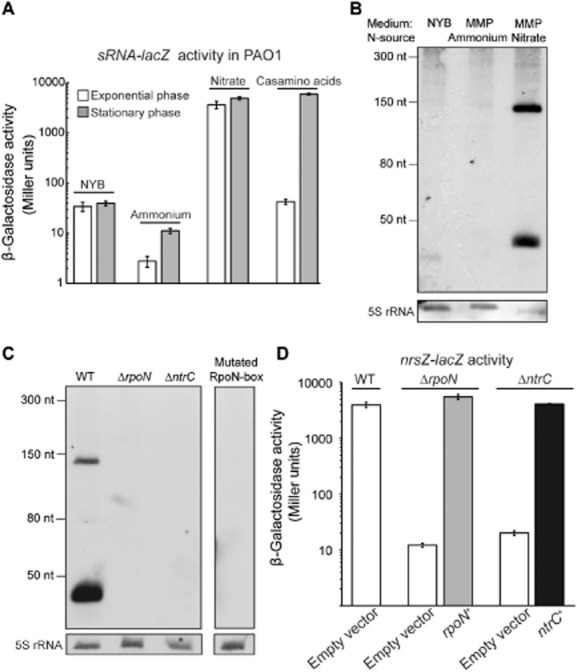
The sRNA NrsZ of P. aeruginosa PAO1 is induced during nitrogen limitation by the NtrB/C-RpoN cascade.
A. β-Galactosidase activities of the chromosomal reporter fusion sRNA-lacZ (nrsZ-lacZ) under various nitrogen-limited conditions. The PAO1 WT strain carrying nrsZ-lacZ (PAO6750) was grown in NYB, MMP supplemented with glucose as carbon source and ammonia, nitrate or casamino acids (0.1%) as nitrogen source. Activity of the nrsZ-lacZ chromosomal fusion was measured in exponential phase and when stationary phase was reached. Each value represents the average of triplicate cultures ± standard deviation.
B. Northern blot detection of the sRNA: RNA was isolated from PAO1 (WT) grown to stationary phase in NYB, MMP supplemented with succinate as carbon source and ammonium or nitrate as nitrogen source. 7.5 μg of cross-linked total RNA was hybridized with the ssRNA probe NrsRNA. As loading control, the membrane was re-probed with the 5SDNA, which detects 5S rRNA.
C. Northern blot detection of the sRNA: Total RNA was extracted from strains PAO1 WT, ΔrpoN (PAO6358), ΔntrC (PAO6764), and from the strain mutated in the RpoN box of the sRNA promoter (PAO6846) grown to stationary phase in MMP supplemented with glucose and casamino acids (0.1%). 5 μg of cross-linked total RNA was hybridized with the ssRNA probe NrsRNA. As loading control, the membranes were re-probed with the 5SDNA detecting the 5S rRNA.
D.β-Galactosidase activities of the chromosomal reporter fusion nrsZ-lacZ in different strains. The WT (PAO6750), ΔrpoN (PAO6847) and ΔntrC (PAO6842) strains carrying the pME6001 empty vector, the strain ΔrpoN complemented with rpoN+ (pME6001::rpoN, pME10389) and the strain ΔntrC complemented with ntrC+ (pME6001::ntrC, pME10390) were grown in MMP supplemented with glucose and casamino acids (0.1%). nrsZ-lacZ activity was measured when stationary phase was reached. Each value represents the average of triplicate cultures ± standard deviation.
