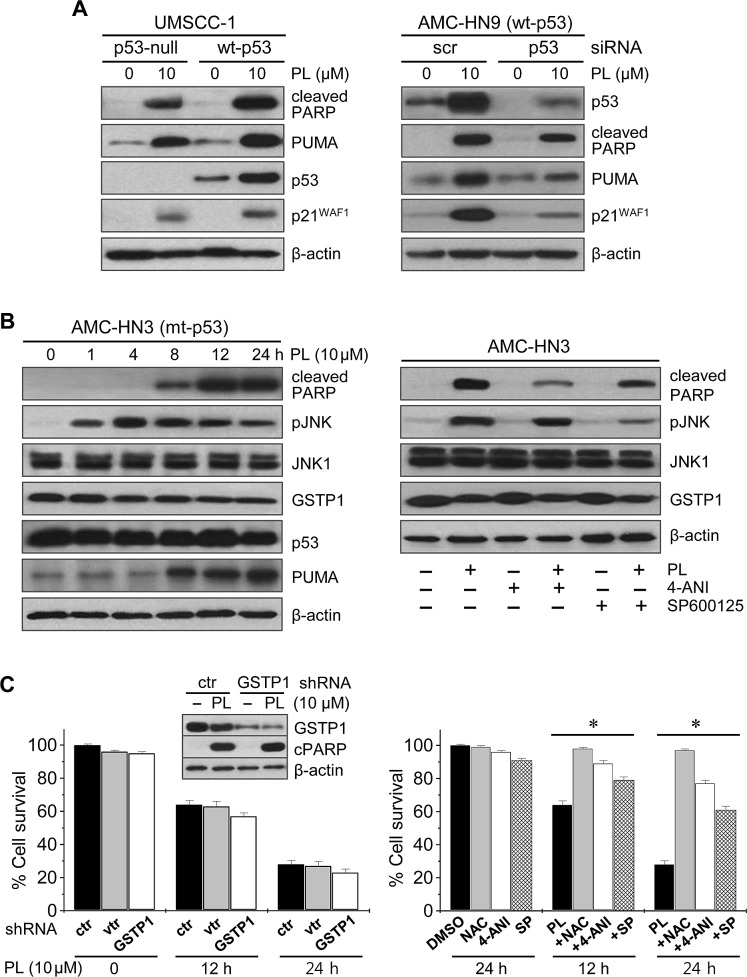
Figure 4. Piperlongumine induces cancer cell death by interfering with ROS regulators.
(A) The effects of PL on p53 and its target proteins, PUMA, cleaved PARP and p21WAF1, were measured by Western blot analysis in cancer cells exposed to 10 μM PL or DMSO (control). Wild-type (wt) p53 was stably transfected in p53-null UMSCC-1 using a retroviral vector. AMC-HN9 cells with wt p53 were transfected with scrambled siRNA (scr) or p53 siRNA for 48 h, prior to PL exposure. (B) Western blot analysis revealing changes in levels of cleaved PARP, phospho-JNK (pJNK), JNK1, GSTP1 and PUMA. Cell extracts were obtained after exposing mutant p53 (mt-p53) AMC-HN3 cells to 10 μM PL (left panel). Cells were also pretreated with 2 μM of the PARP inhibitor 4-ANI for 16 h or 20 μM of the JNK inhibitor SP600125 for 1 h before exposure to 10 μM PL for 12 h (right panel). (C) Effects of GSTP1 knockdown and PARP or JNK inhibition on PL-induced changes in cell growth. AMC-HN3 cells were stably transfected with GSTP1 shRNA or control shRNA in a lentiviral vector (vtr). The knockdown was confirmed by Western blotting using anti-GSTP1 antibody. Cell viability was measured by trypan blue exclusion in parental HN3 cells and sublines (left panel), and in AMC-HN3 cell lines exposed to 10 μM PL or to the combination of 10 μM PL and 3 mM NAC, 2 μM 4-ANI, or 20 μM SP600125 (SP) (right panel). The error bars represent the s.d. from three independent experiments, each performed with triplicate samples. * denotes p < 0.01.