Figure 4. Magnitude of increase in sympathetic vasoconstriction during selective nNOS inhibition (grey bars) and non-selective NOS inhibition (hatched grey bars) at rest (A) and during muscular contraction (C).
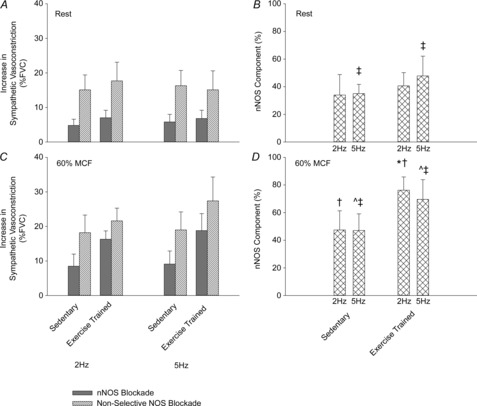
Contribution of NO derived from nNOS to total NO-mediated inhibition of sympathetic vasoconstriction at rest (B) and during muscular contraction (D). Values are means ± s.d. Main effect of ^muscle contraction and ‡exercise training. *Significant difference between exercise-trained and sedentary rats. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. FVC, femoral vascular conductance; MCF, maximal contractile force; nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase.
