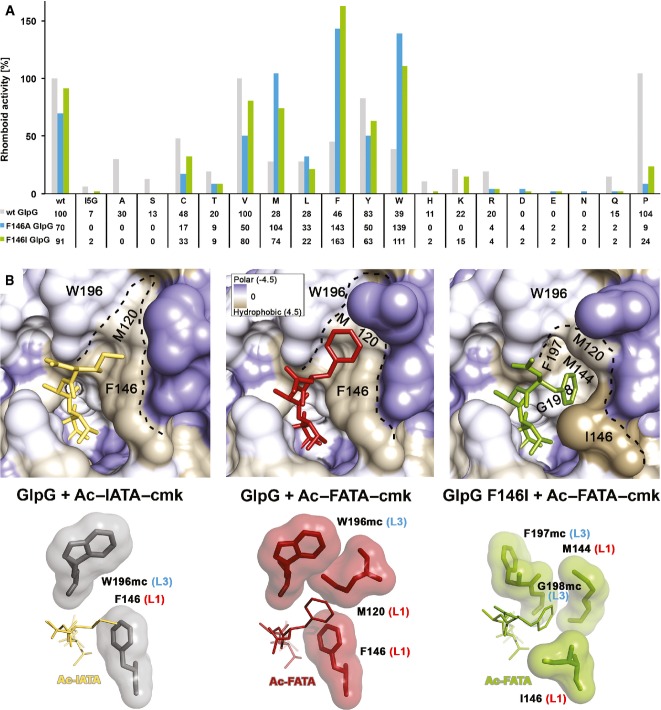
Figure 4. A patch of hydrophobic residues from the L1 loop forms the S4 subsite of GlpG.
A Compensatory effect of mutations in the S4 subsite of GlpG and the P4 position of TatA. Mutation of the S4 subsite residue F146 to the smaller hydrophobic residues alanine or isoleucine is nearly or completely inactivating only for substrate variants with small- to medium-sized side chains (A, S, C, T, V, I) in the P4 position. This attenuating effect of the GlpG S4 subsite mutants can be compensated by a mutation of the TatA P4 residue to a residue with a bigger side chain. Hence, while wild-type (F146) GlpG cleaves the TatA substrate with a large P4 residue (such as I5W) very poorly, the activity can be fully recovered by replacing the bulky phenylalanine 146 in the S4 subsite of the enzyme by a small hydrophobic side chain (such as F146A). The assays have been conducted three times independently, and representative data are shown (source data in Supplementary Fig S7).
B The S4 subsite in the complex structures GlpG:Ac-IATA-cmk, GlpG:Ac-FATA-cmk and GlpG_F146I:Ac-FATA-cmk. Crystallographic statistics are shown in Supplementary Table S1. Upper panels: close-up view of the S4 subsite with the surface of GlpG coloured according to the Kyte-Doolittle hydrophobicity scale (Kyte & Doolittle, 1982). The S4 subsite is a surface-exposed hydrophobic patch formed by residues from the L1 loop. Lower panels: residues making vdW interactions with the bound tetrapeptide are shown as contact surfaces. For residues W196, F197 and G198 of the L3 loop, only main chain atoms (mc) are engaged in interactions. Residues F146, M120, M144 and I146 of the L1 loop make vdW contacts with their side chains. The isoleucine in the P4 position of Ac-IATA forms a CH-π interaction with the aromatic side chain of F146.