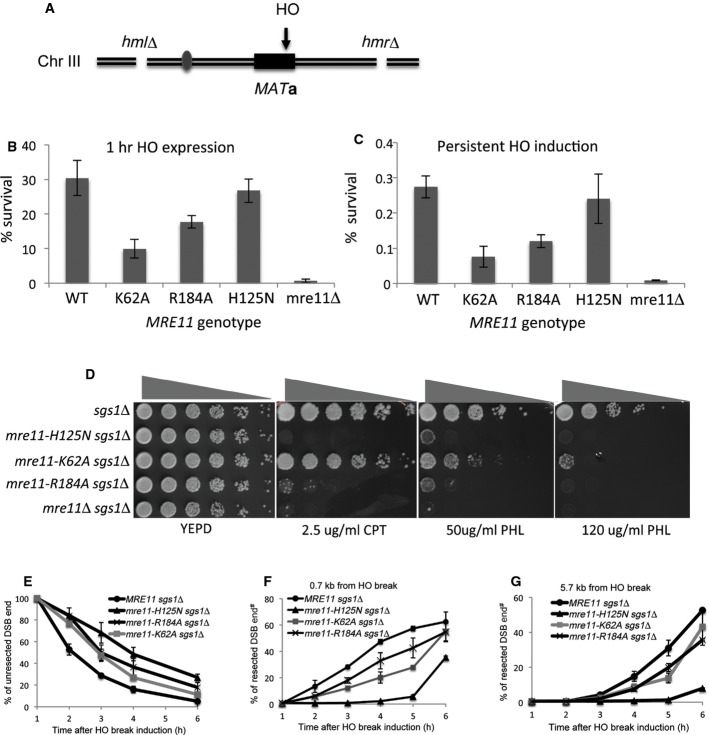
Figure 5. Analysis of mre11 mutants in vivo.
A Schematic illustration of the NHEJ assay.
B, C NHEJ proficiency of yeast mutants was determined by measuring their survival rate upon induction of an HO break at the MAT locus. Deletion of HML and HMR forced repair of this DSB to occur by NHEJ only. Survival rate was calculated by dividing the number of colonies on YEP-galactose or YEPD following addition of galactose, by the number of colonies on YEPD on which HO was not induced. Survival of SLY1 (MRE11+, JKM139 derivatives), mre11Δ, mre11-K62A, mre11-K184A, and nuclease-deficient mre11-H125N (B) after expression of HO endonuclease for 1 h or (C) continuously by plating onto YEP-galactose plates is shown. Each point represents the average of at least three independent experiments ± SD.
D Sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents. Fivefold serial dilutions of nuclease-deficient mre11–H125N and mre11 variants with mutations at the putative DNA-binding interface (K62A, and R184A, JKM139 derivatives) were spotted onto YEPD plates with the indicated doses of genotoxic drugs and incubated for 2–3 days before being photographed. Drug sensitivity assays were also performed on strains deleted for SGS1, in which redundant resection pathways have been disabled. CPT, camptothecin; PHL, phleomycin. Shown is an example of spot assays performed three times independently.
E A graph showing the amount of un-resected DNA, measured by a Southern blot-based resection assay, in SLY1A (MRE11+, JKM139 derivatives) and mre11 mutant derivatives. Each point represents the average of at least three independent experiments ± SD.
F, G Graphs showing the amount of ssDNA at 0.7 or 5.7 kb distal to a DSB, measured by a PCR-based DNA resection assay. Each point represents the average of at least two independent experiments.