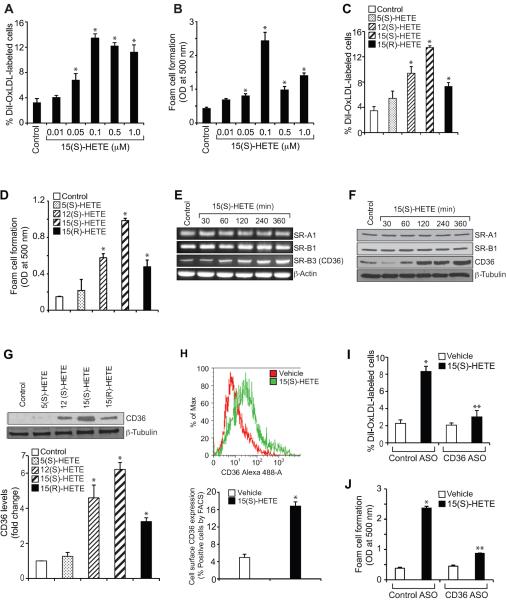
Figure 1.
15(S)-HETE induces OxLDL uptake and foam cell formation via CD36 expression. A–D. Quiescent THP1 cells were treated with vehicle or the indicated doses of 15(S)-HETE or 0.1 μM of the indicated HETE for 4 hrs and subjected to Dil-OxLDL uptake (panels A & C) and foam cell formation (panels B & D) as described in “Materials and Methods.” E–G. Quiescent THP1 cells were treated with vehicle or 0.1 μM 15(S)-HETE for the indicated time periods or 0.1 μM of the indicated HETE for 4 hrs and either RNA was isolated or protein extracts were prepared. The RNA and protein extracts were analyzed by RT-PCR and Western blotting for the indicated scavenger receptor mRNA (panel E) and protein (panels F & G) levels using their specific primers and antibodies, respectively, and normalized to β-actin mRNA and β-tubulin protein levels, respectively. H. After treatment of quiescent THP1 cells with vehicle or 15(S)-HETE (0.1 μM) for 4 hrs, the cell surface CD36 expression was measured by FACS analysis. A representative histogram is shown in the upper panel and the quantitative analysis is shown as a bar graph in the lower panel. I & J. THP1 cells were transfected with the indicated ASO, quiesced, treated with vehicle or 0.1 μM 15(S)-HETE for 4 hrs and subjected to Dil-OxLDL uptake (panel I) and foam cell formation (panel J) as described in “Materials and Methods”. The bar graphs represent Mean ± SD values of three experiments. *, p<0.01 versus vehicle control or control ASO; **, p<0.01 versus 15(S)-HETE or control ASO + 15(S)-HETE.