FIGURE 1.
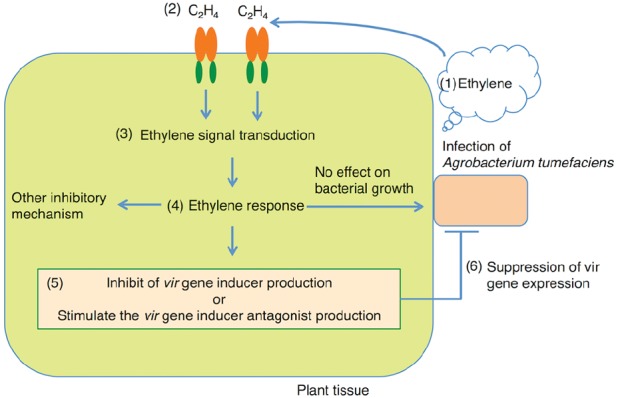
Schematic drawing of the potential mechanisms of inhibition through ethylene signaling and vir gene expression. (1) The infection of A. tumefaciens induces ethylene evolution from plant tissue. (2) Ethylene is received by the ethylene receptor. (3) Ethylene signal transduction is induced and, (4) subsequently, the plant shows the ethylene response. (5) In plants that show the ethylene response, vir gene inducer production would be suppressed or an antagonist of the inducer would be produced, (6) resulting in a reduction of vir gene expression in A. tumefaciens.
