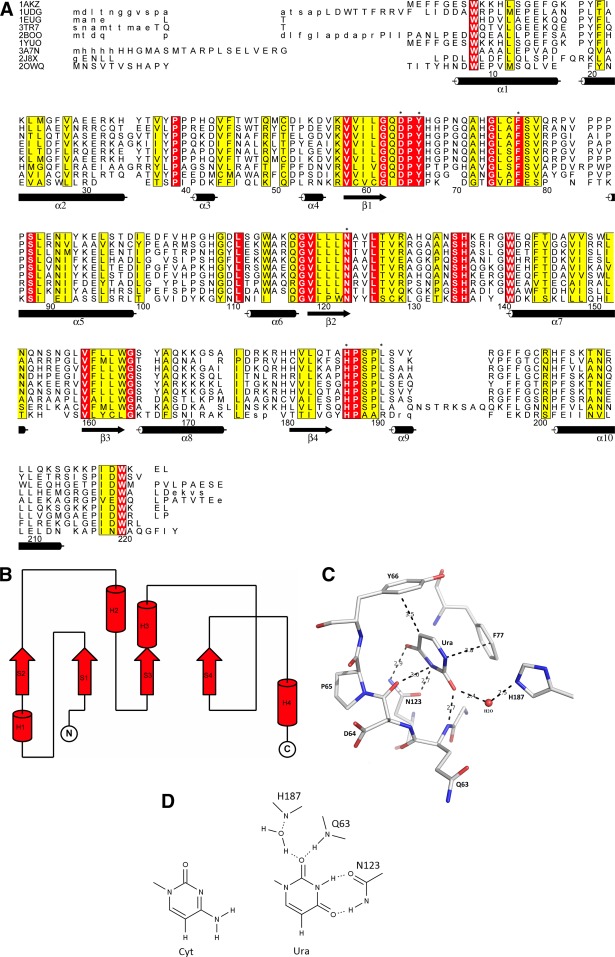
Figure 3.
A. Structure-based sequence alignment for UNG subfamily. The secondary structure assignment is based on hUNG [1AKZ]. Residue numbering in this alignment is arbitrary (the first residue in 1AKZ is set to 1). Highlighted (*) are the six active site residues. Identical residues are shaded in red while similar residues are shaded in yellow. The largest differences are observed for vUNG [2OWQ]. B. Topology of UNG. The topology diagram highlights the basic fold: three layers a/b/a (two α-helices on either side of the core of four parallel β-strands in the order 2134). C. Active site (tertiary structure) in UNG. Active site in eUNG [2EUG] highlighting the observed interactions (dashed lines in black) of uracil (Ura) with active site residues. Hydrogen-bonding and van der Waals distances (in Å) are shown. Active site residues and Ura are represented as stick models (C grey, O red, N blue) and labeled. A conserved water molecule in the active site is shown as a red sphere. D. Schematic active site interactions in UNG. Schematic of uracil (Ura) interactions (hydrogen-bonding network) in the binding pocket of UNG (eUNG). Comparison with cytosine (Cyt) in the same orientation illustrates that the same type of hydrogen bonds with Asn123 as seen for Ura are not possible.