Fig. 2.
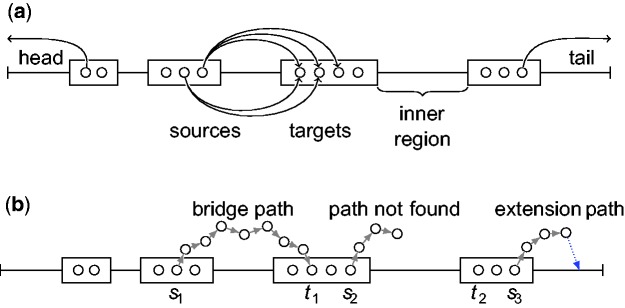
Long read correction method. (a) A long read is partitioned into weak and solid regions (respectively, lines and rectangles) according to the short read DBG. Weak regions starting or ending the long read are called the head or the tail, respectively, while other weak regions are inner regions. Circles in solid regions represent k-mers of the DBG. k-mers around a weak region serve as source and target nodes to search paths in the DBG. Several source/target pairs are used for each weak inner region. (b) On the second inner region, a bridging path between nodes s1 and t1 is found in the DBG to correct this region. On the third region, the path search fails to find a path between nodes s2 and t2. For the tail, an extension path is sought and found from node s3 toward the end. Once found, the corrective sequence of the path is aligned to the tail to determine the optimal substring (thick dotted arrow)
