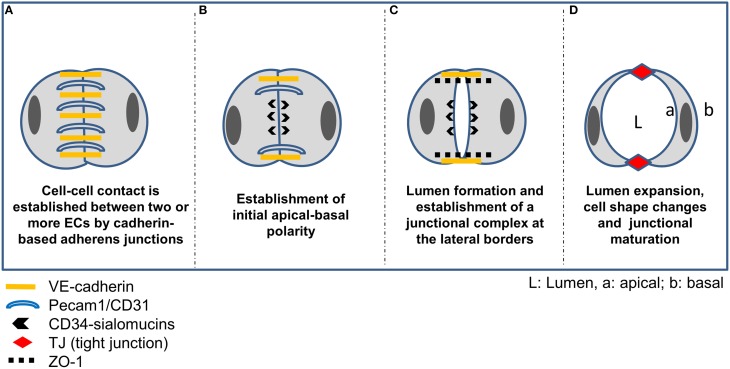
Figure 2.
Vascular lumen formation by cord hollowing. (A) Intercellular adhesion of two or more ECs is accomplished by homophilic interaction of VE-cadherin and Pecam-1. (B) Following establishment of Par3-mediated apicobasal polarity via ß-1 integrin matrix interaction and the adaptor protein RASIP1, CD34-sialomucins (CD34 and podocalyxin; PODXL) are recruited to cell-cell contacts delineating the future apical border. VE-cadherin is required for specifically targeting CD34-sialomucins to contact sites, and the delivery depends on PTEN-mediated transformation of PIP3 to PIP2. Rasip1 localizes at inter-endothelial junctions and acts downstream of Rap1 (Ras-related protein1), mediating EC-ECM adhesion and stabilizing junctional integrity by actin bundling. In cooperation with Radil (ras-association and dilute domain-containing protein), Rasip1 further inhibits Rho-mediated stress fiber formation, thereby increasing endothelial barrier function. Further, CCM1 mediates the stabilization of β-catenin-containing endothelial cell-cell junctions downstream of the Rap1 GTPase. (C) Due to the negatively charged CD34-sialomucins, electrostatic repulsion leads to separation of the contacting plasma membranes thereby creating a free (non-contacting) surface and a small lumen between ECs. Concomitantly, cadherin-based AJs are redistributed to lateral borders, indicating the establishment of a lateral junctional complex. Following phosphorylation by protein kinase C, pMoesin, the major ERM protein in endothelial cells, is recruited to the future apical membrane and links CD34-sialomucins to F-actin, supporting cytoskeletal rearrangements in ECs during lumen expansion. Further, non-muscle myosin assembles at the apical plasma membrane and interacts with F-actin in response to VEGF signaling to support lumen expansion and cell shape changes. (D) Further maturation of the endothelial TJs is then mediated by claudin-5, occludin, members of the junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) family, or by EC-selective adhesion molecule (ESAM).