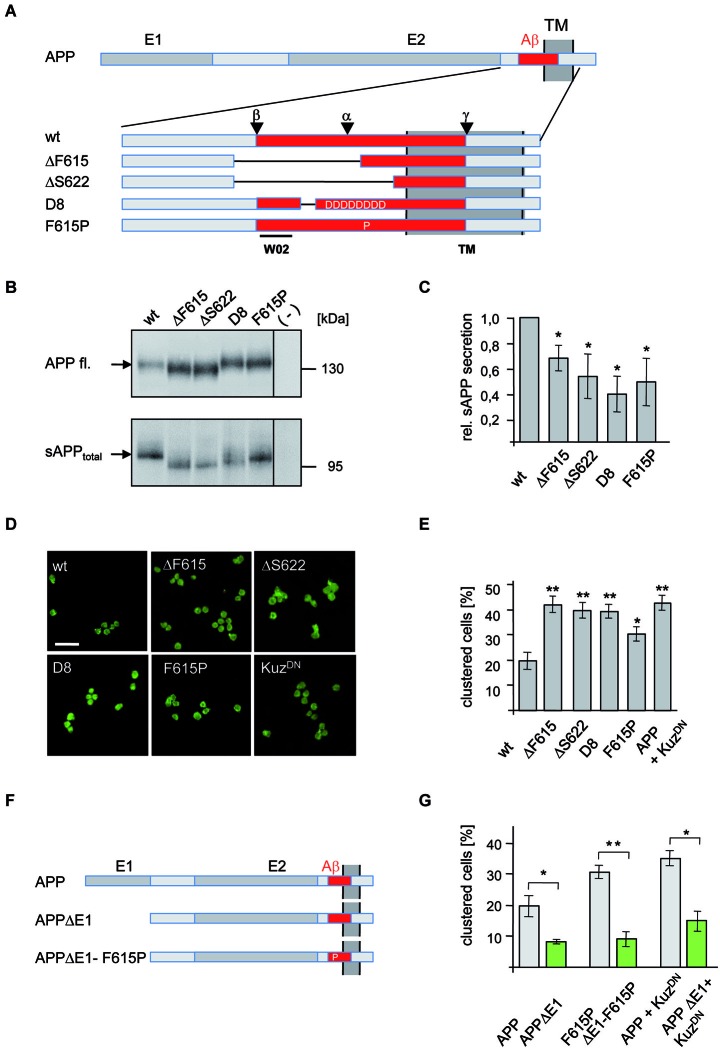
Figure 1.
Analysis of APP secretion deficient mutants in Drosophila S2 cells. (A) Schematic representation of N-terminally myc tagged APP secretion deficient constructs. The E1 and E2 domain as well as the transmembrane (TM) domain are highlighted in dark gray. The Aβ region of APP (red) is shown enlarged and the position of deletions and amino acid substitutions is given. Additionally, positions of α-, β-, and γ-cleavage sites are indicated as well as the epitope of antibody W02 (aa 2–8). Deletions of the APP mutants are marked with lines. (B) Western Blot analysis of sAPPtotal secretion from transfected S2 cells expressing APPwt and mutant variants. Direct load of cellular extracts and medium-IP (22734) samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibody 22C11. (C) Densitometric quantification of sAPPtotal/APP fl. ratio (t-test, n ≥ 3, ±SEM). (D) S2 cells, transiently transfected with APPwt or secretion deficient APP-mutants were aggregated and immunostained with an anti c-myc antibody. Scale bar: 20 μm. (E) Quantification of clustered wild type APP and mutant APP expressing S2 cells (t-test, n ≥ 5; ± SEM); (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.001; *** p < 0.0001). (F) Scheme of APP mutants lacking the E1 domain. (G) S2 cells were transiently transfected with human APPwt or secretion deficient APP-F615P and the corresponding E1-deletion constructs (APPΔE1, APP-F615PΔE1) or co-transfected with APPwt or APPΔE1 and a dominant negative form of Kuzbanian (KuzDN). Cells were aggregated and immunostained with anti c-myc antibody showing that secretion deficient APP cell-clustering depends on the E1-domain. Quantification of clustered cells given as percentage of the amount of transfected cells (t-test, n ≥ 5; ± SEM; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.001; *** p < 0.0001).