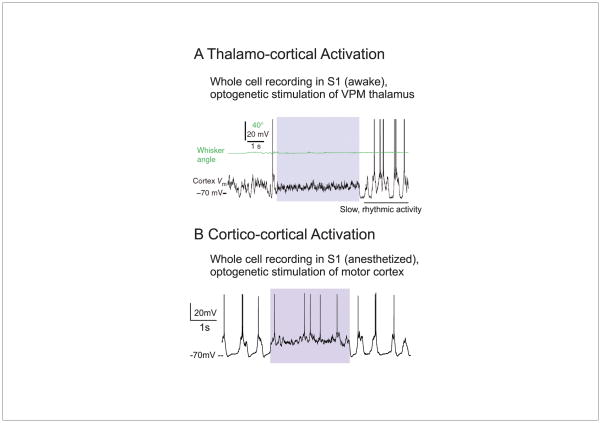
Figure 3.
The stimulation of glutamatergic pathways can result in the rapid activation of cortical networks. A. Whole cell recording from a cortical pyramidal cell during the optogenetic stimulation of thalamus (colored box). During thalamic stimulation, the cortical neuron is rapidly and tonically depolarized and slow fluctuations are suppressed. B. A similar effect is observed upon stimulation of feedback projections from primary motor cortex (M1) to primary somatosensory cortex (S1). Note that both responses exhibit rapid onset and offset kinetics and result in changes in cortical network activity that is similar to arousal, movement, and attention. A is from [14]; B is from [8].