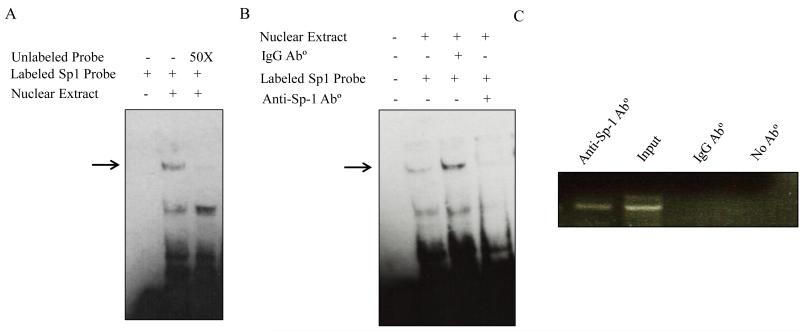
Fig. 4. Binding of Sp-1 transcription factor to the SLC52A1 promoter in vitro and in vivo.
A. DNA/protein profile from EMSA using the SLC52A1 minimal promoter region. Gel shift assays were conducted with HuTu 80 cells nuclear extract as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS section. The labeled fragment of the SLC52A1 promoter region (−60/−33) was used. DNA/protein complexes were resolved on 6% retardation acrylamide gel. Competition experiments were performed using a 50 fold molar excess of unlabeled promoter fragment. The specific complex is indicated with an arrow. B. Presence of Sp1 in DNA-protein complexes. Nuclear extracts were pre-incubated with anti-Sp-1 antibody or nonspecific IgG before the addition of the biotin labeled Sp-1 probe. Data are representative of three separate experiments. C. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis. Formaldehyde cross-linked chromatin from HuTu 80 cells was incubated with anti-Sp-1 antibody. As a negative control, the chromatin was incubated without antibodies or with nonspecific IgG antibody. Total input DNA at a 1:10 dilution was used as a positive control for the PCR reaction. Immunoprecipitated DNA was analyzed by PCR with primers specific for the SLC52A1 promoter.