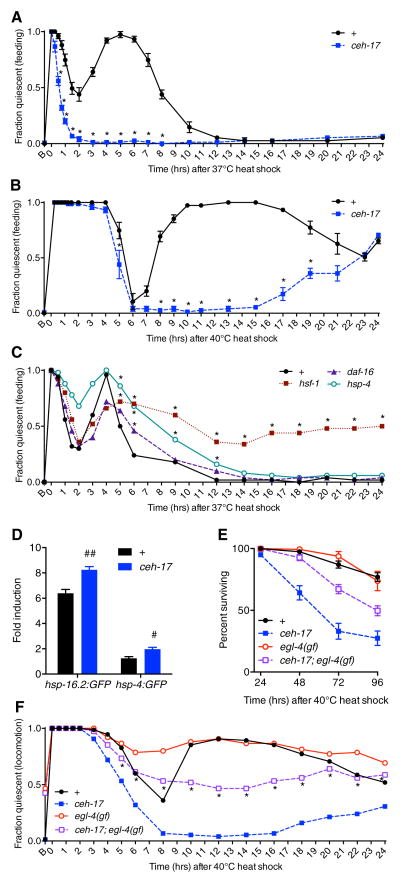
Figure 4.
Recovery quiescence is associated with restoration of proteostasis and survival following noxious heat exposure. A and B, Time course of feeding quiescence in wild-type and ceh-17(np1) animals following a 30 min 37°C heat shock (A) and a 20 min 40°C heat shock (B). *p < 0.001; Fisher’s exact test. C, Time course of feeding quiescence in wild-type, hsf-1(sy441), daf-16(mu68), and hsp-4(gk514) animals following a 30 min 37°C heat shock. Peak quiescence is reduced in hsf-1 and daf-16 mutant animals compared to wild type (asterisks not shown, p = 0.0019 in both cases; Fisher’s exact test), while the duration of quiescence is significantly increased (*p < 0.05; Fisher’s exact test.) in each of the mutant strains. For panels A–C, feeding quiescence is shown but animals were similarly quiescent for locomotion. D, Fold expression of hsp-16.2:GFP and hsp-4:GFP transcriptional reporters 24 hours after a 37°C 30 min heat shock compared to untreated controls. #p < 0.01, ##p < 0.001; Student’s t test. E and F, Survival (E) and locomotor quiescence (F) among wild-type, ceh-17(np1), egl-4(ad450gf), and ceh-17(np1);egl-4(ad450gf) animals following a 20 min 40°C heat shock. ceh-17 animals are significantly impaired for survival compared to wild type (p < 0.001; log rank test). In ceh-17;egl-4(gf) mutants, locomotor quiescence is partially restored (*p < 0.05 vs. ceh-17(np1); Fisher’s exact test) and the survival defect is partially rescued (p < 0.001 vs. ceh-17(np1); log rank test). egl-4(gf) animals do not show significantly greater survival than wild-type animals (p = 0.647; log rank test) but display increased quiescence at certain time points (p < 0.05 vs. wild type at 6, 8, 22, and 24 hrs after heat shock; Fisher’s exact test). Mean and SEM are shown for all panels except C and F, which show mean only. On the X axes, “B” indicates baseline (untreated).