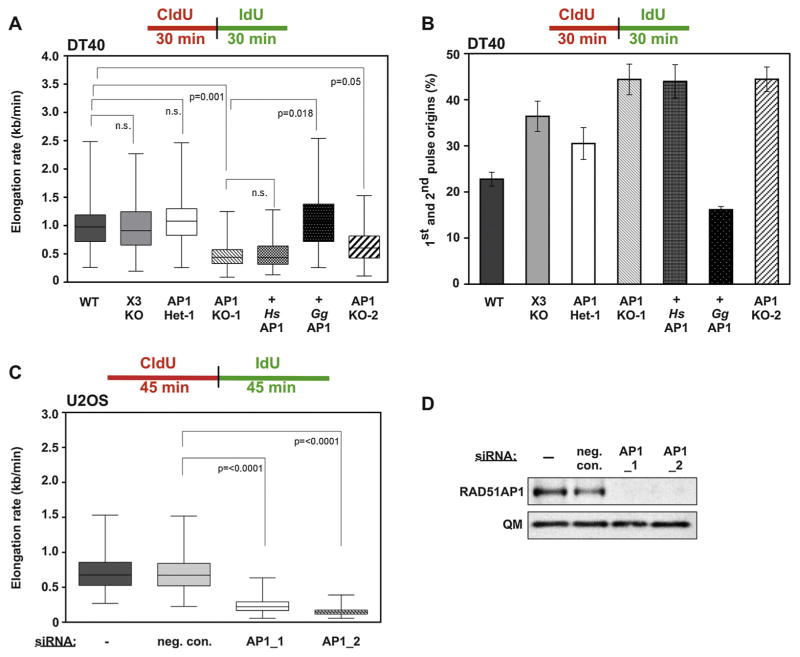
Fig. 3.
RAD51AP1 is required to maintain the progression of DNA replication forks and to suppress dormant origin firing. (A) RAD51AP1-deficient DT40 cells show greatly reduced DNA elongation rates under unperturbed conditions. Ectopic expression of GgRAD51AP1 (here: + GgAP1), but not of HsRAD51AP1 (here: + HsAP1) reverts elongation rates back to wild type levels. In box plots, boxes encompass the 25th–27th percentile, with error bars defining the minima and maxima. The black horizontal bars within the boxes indicate the means. (B) RAD51AP1-deficient DT40 cells show enhanced levels of first and second pulse replication origins under unperturbed conditions. Ectopic expression of GgRAD51AP1 (here: + GgAP1), but not of HsRAD51AP1 (here: + HsAP1) reverts origin firing close to the levels of wild type cells. (C) RAD51AP1-depleted U2OS cells show greatly reduced DNA elongation rates under unperturbed conditions. Knockdown of RAD51AP1 was obtained by transfection with one of the two different siRNAs targeting RAD51AP1. NCS: non-depleting control siRNA. In box plots, boxes encompass the 25th–27th percentile, with error bars defining the minima and maxima. The black horizontal bars within the boxes indicate the means. (D) Representative Western blots obtained for the experiments shown in (C).