Figure 2.
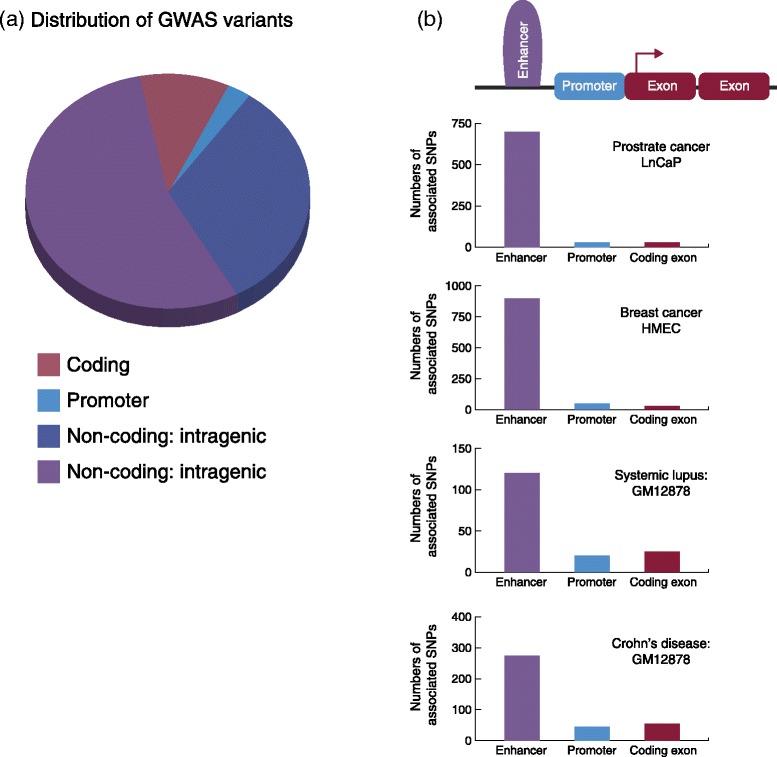
Enrichment of genome-wide association study variants in putative enhancer elements. (a) Number of disease-associated variants (identified in the National Human Genome Resource Institute’s genome-wide association study (GWAS) catalog) that lie in protein-coding regions (red), promoters (blue), noncoding intragenic regions (light purple) and noncoding intergenic regions (dark purple). (b) Examples of four different common diseases, showing the number of associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that lie in putative enhancers, promoters and exons [6-8]. Putative enhancer elements were defined by chromatin features in each of the four indicated cell types.
