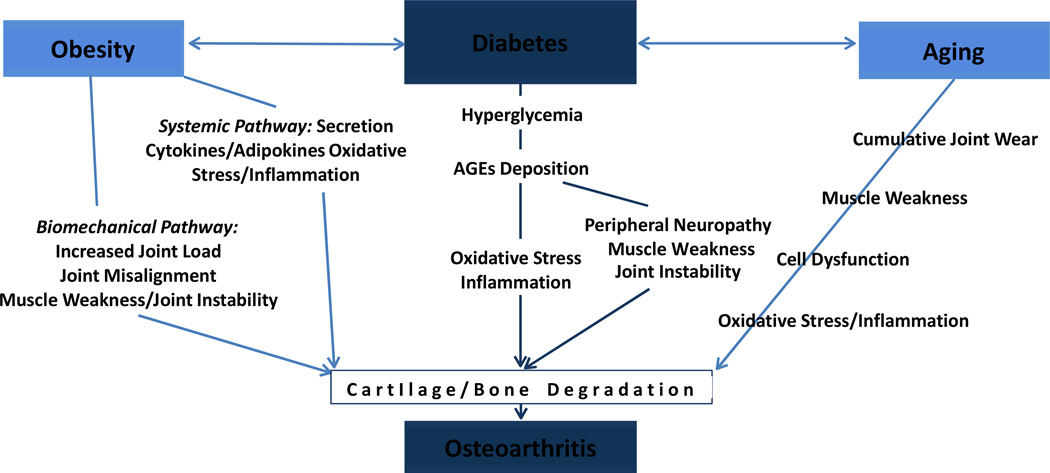
Figure 1. Common Risk Factors of OA and T2DM.
Obesity and age are well-established shared risk factors for OA and T2DM. Obesity affects OA through biomechanical and systemic pathways. Age affects OA by factors such as cumulative joint load, muscle weakness, cell dysfunction (e.g., chondrocyte, mitochondria), and chronic inflammation. T2DM seems to have a direct impact on OA as hyperglycemia promotes deposition of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) and affects cartilage health. Hyperglycemia also contributes to peripheral neuropathy, which can contribute to muscle weakness, joint instability, and consequent OA of weight-bearing joints.