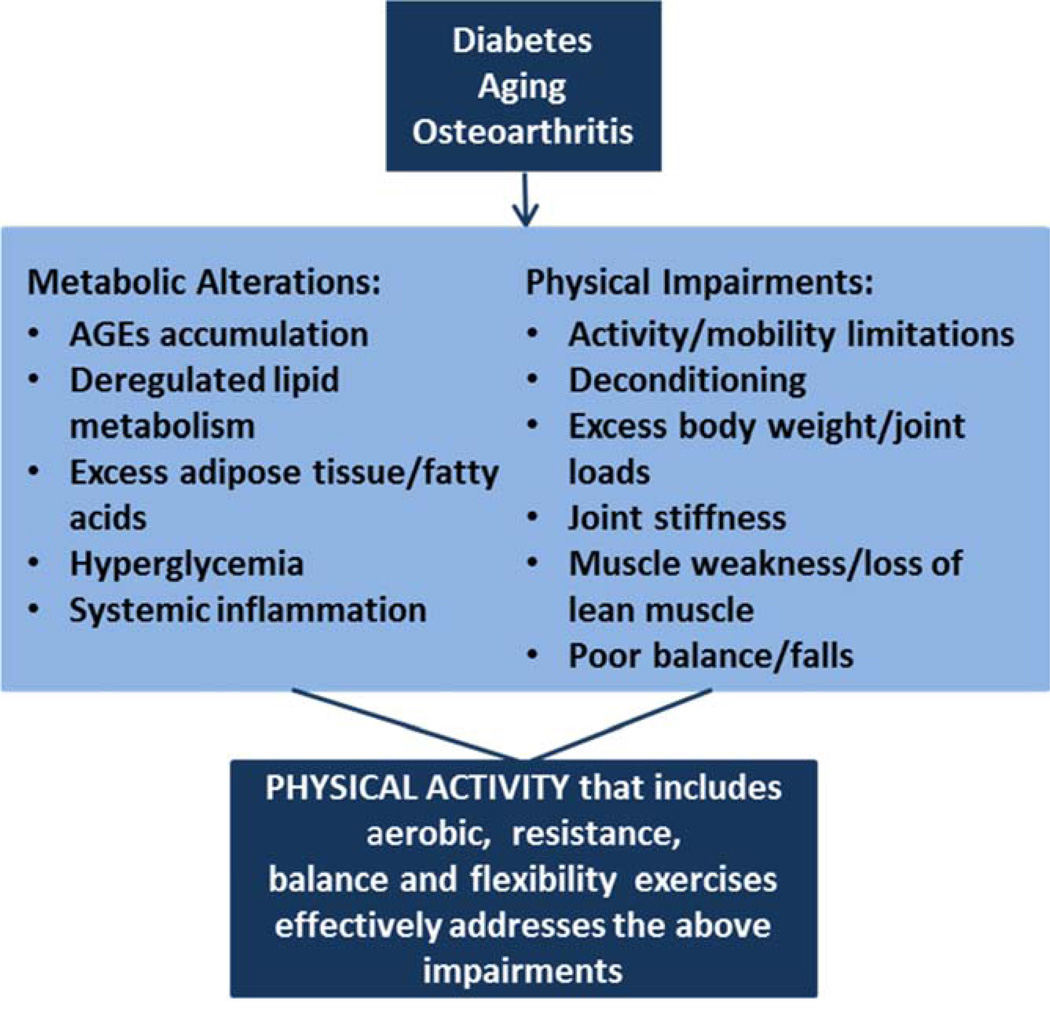
Figure 2. Physical and Metabolic Impairments Resultant of T2DM, Aging and OA that Can Benefit from Physical Activity.
T2DM, aging and OA are associated with several physical impairments and metabolic alterations that can be addressed by physical activity. Physical impairments common in this population include: excess body weight and consequent increased adiposity and joint loads; poor balance and increased fall risk; muscle dysfunction such as muscle weakness, muscle atrophy, and decreased lean muscle mass; pain and joint stiffness; all of these impairments limit daily activities and mobility. Metabolic alterations include hyperglycemia, excess adipose tissue with deregulated lipid metabolism, accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), and systemic inflammation.