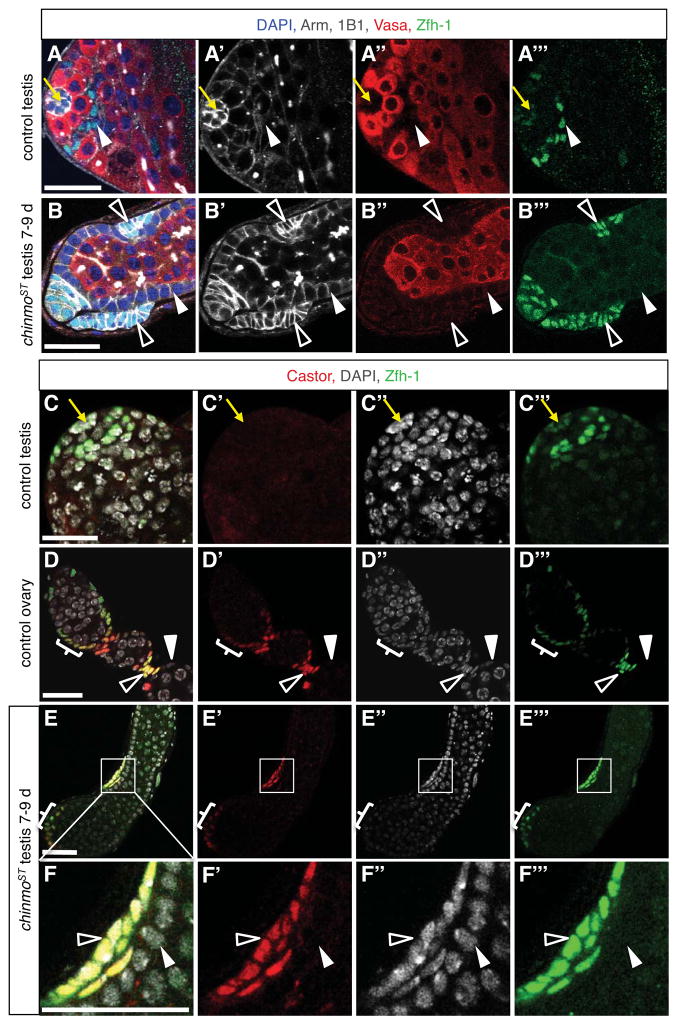
Figure 4. Ovarian stalk cell markers are expressed in a subset of somatic cells in chinmoST testes.
(A–B) Immunofluorescence detection of Arm (white) and Zfh-1 (green) reveals stalk-like cells in chinmoST testes. In control testes (A), hub cells (yellow arrow) express high levels of Arm and low levels of Zfh-1, and CySCs and their immediate daughters (arrowhead) express low levels of Arm and high levels of Zfh-1. In all other cyst cells, Arm is low and Zfh-1 is absent. In chinmoST testes (B), Arm is low and Zfh-1 is absent in follicle-like cells lining the periphery (solid arrowhead). Other somatic cells (open arrowheads) form aggregates that resemble ovarian stalk cells morphologically and express high levels of Arm and Zfh-1, which are characteristic of stalk cells (data not shown). These aggregates are typically located just beneath the testis sheath, sandwiched between follicle-like cells and the basement membrane. (C–F) Immunofluorescence detection of Castor (red) and Zfh-1 (green) reveals stalk-like cells in chinmoST testes. Castor is absent from control testes (C; also see Fig. 2A). Hubs marked by yellow arrow. In control ovaries (D), Castor is expressed in follicle stem cells and early follicle cell progenitors (bracket; also see Fig. 2C). After egg chamber formation, Castor is restricted to polar cells and Zfh-1+ stalk cells (open arrowhead) and is no longer expressed in main-body follicle cells (solid arrowhead). In chinmoST testes (E–F), Castor is expressed in Zfh-1+ cell aggregates at the testis apex that resemble follicle cell progenitors (bracket) and in stalk-like cells (open arrowheads) but not in Zfh-1− follicle-like cells (solid arrowhead). Panel F is an enlargement of the boxed area in panel E. Scale bars = 20 μm.