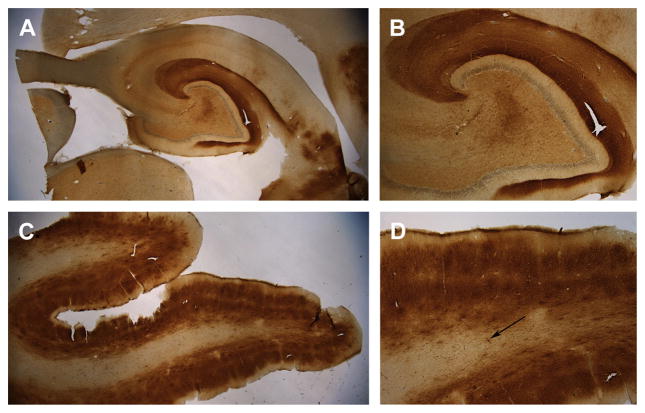
Fig. 1.
Aβ immunostaining (brown) in the brain of a 14-year-old border collie (Martha) with signs of cognitive dysfunction syndrome. Aβ was detected using the 6E10 antibody that binds Aβ 1 to 16. (A) Low-power magnification (1.5×) of extensive Aβ deposition in the hippocampus. (B) Aβ is primarily found in the outer molecular layer of the dentate gyrus, which contains neuron terminals originating from the entorhinal cortex (4×). (C) The prefrontal cortex also shows extensive Aβ deposition that appears most dense in layers II and V of the cortex and is less apparent in the white matter (1.5×). (D) At high magnification (4×), the differential deposition of Aβ in the 6 cortical layers can be seen as well as extensive white matter cerebral amyloid angiopathy (arrow). Sections have been counterstained with cresyl violet (blue).