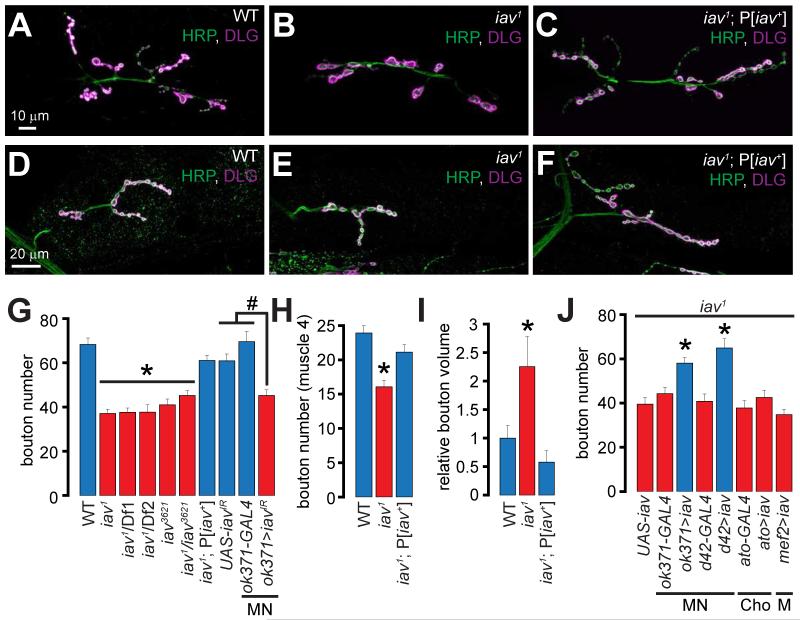
Figure 1. Alterations in synaptic growth and morphology in iav1.
(A-C) Confocal images of NMJs on muscles 6/7 from larvae of the indicated genotypes stained with antibodies against the presynaptic marker, HRP (green) and the postsynaptic marker, DLG (magenta). Scale bar shown in (A) also applies to (B-C).
(D-F) Confocal images of NMJs on muscle 4 from larvae of the indicated genotypes stained with antibodies against HRP (green) and DLG (magenta). Scale bar shown in (D) also applies to (E-F).
(G) Quantification of the number of boutons at NMJs on muscles 6/7 in larvae of the indicated genotypes. *, p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA (comparing all the iav1 alleles with WT and iav1;P[iav+]; #, p = 2.5×10−5, one-way ANOVA (comparing ok371>iavIR with GAL4 and UAS controls); n=8-30 NMJs per genotype.
(H) Quantification of the number of boutons at NMJs on muscle 4 in larvae of the indicated genotypes. *, p = 6.3×10−6, one-way ANOVA (comparing all the data sets shown), n=8-14 NMJs per genotype.
(I) Quantification of the volume/bouton in larvae of the indicated genotypes. *, p = 0.007, one-way ANOVA (comparing all the data sets shown), n≥7 NMJs per genotype.
(J) Quantification of the bouton number in larvae of the indicated genotypes. *, p <10−6, one-way ANOVA (comparing the data sets shown in the blue bars with those in the red bars), n=11-20 NMJs per genotype.
All values represent mean ±SEM. Please consult Supplementary Files for values. Abbreviations: MN, motor neuron; Cho, chordotonal organ; M, muscle.