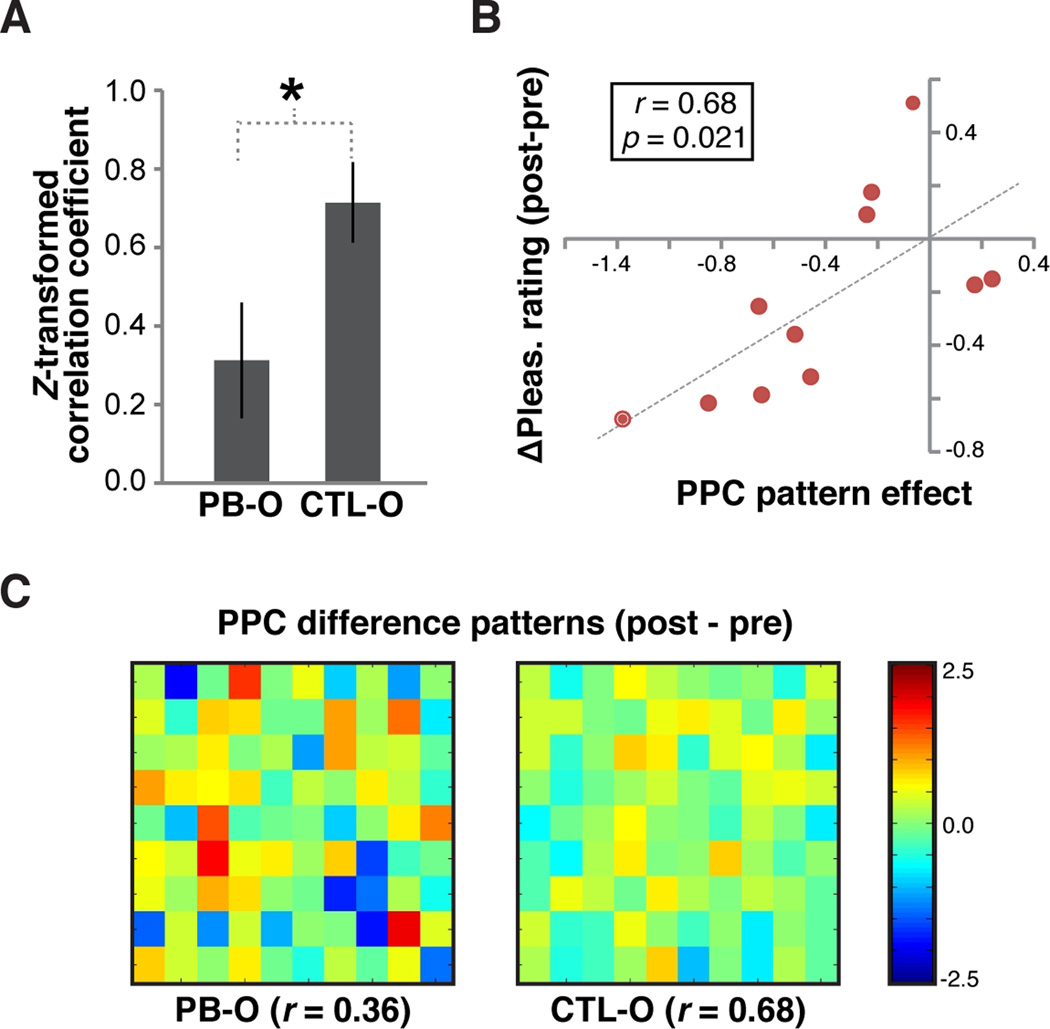
Figure 3. Satiety-related effects on fMRI pattern ensemble activity evoked by the whole odor.
(A) Subject-average correlation (Fisher z-transformed) between pre-satiety patterns and post-satiety patterns for PB-O and CTL-O in PPC, indicating greater pattern divergence for PB-O. (B) Relationship between PPC pattern effect (PB-O correlation coefficient minus CTL-O correlation coefficient) and satiety-related behavioral effects. Each dot on the scatter plot represents data from one subject. (C) Difference maps from a representative subject. Each pixel on the map represents one voxel in the PPC ROI. Pre-satiety PPC patterns of activity were subtracted from post-satiety patterns. The correlation value between the two patterns is shown below the difference map. Error bars = across-subject s.e.m., *p < 0.05, paired T-test.