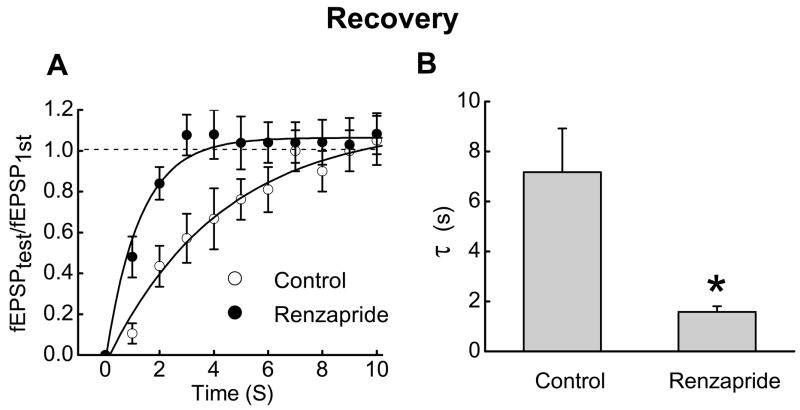
Fig. 2.
Renzapride accelerates recovery of fEPSP amplitude after rundown. A. Time course of recovery of fEPSP amplitude after rundown. Data points are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 10). Recovery is expressed as the ratio of fEPSPtest to fEPSPfirst where fEPSPfirst is the first fEPSP in the stimulus train and fEPSPtest is fEPSP amplitude at various times after the end of the stimulus train. Solid lines are monoexponential fits to the data points. B. Renzapride shortened the time constant (τ) for full recovery of fEPSP amplitude. Data are the mean ± s.e.m. of the recovery time constant determined from monoexponential fits of the recovery time course before and during renzapride (0.1 μM)(n = 10) application. *Indicates different from control (P < 0.05)