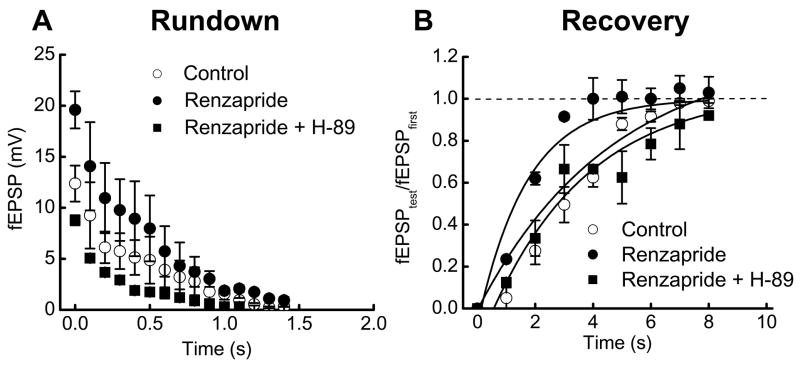
Fig. 5.
The PKA inhibitor, H-89, blocks the effects of renzapride on fEPSPs during and after trains of stimulation. A. Renzapride (0.1 μM) fEPSPs throughout the stimulus train (10 Hz) and H-89 (10 μM) blocked this effect. Renzapride or renzapride with H-89 did not alter the time constant of synaptic rundown. Data are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3) B. Renzapride accelerated recovery after fEPSP rundown. Recovery at each time point was expressed as the ratio of fEPSPtest to fEPSPfirst where fEPSPfirst is the first fEPSP in the stimulus train and fEPSPtest is the amplitude of the fEPSP evoked at various times after the end of the stimulus train. The renzapride induced decrease in the recovery time constant was blocked by H-89. Solid lines are monoexponential fits to the data points.