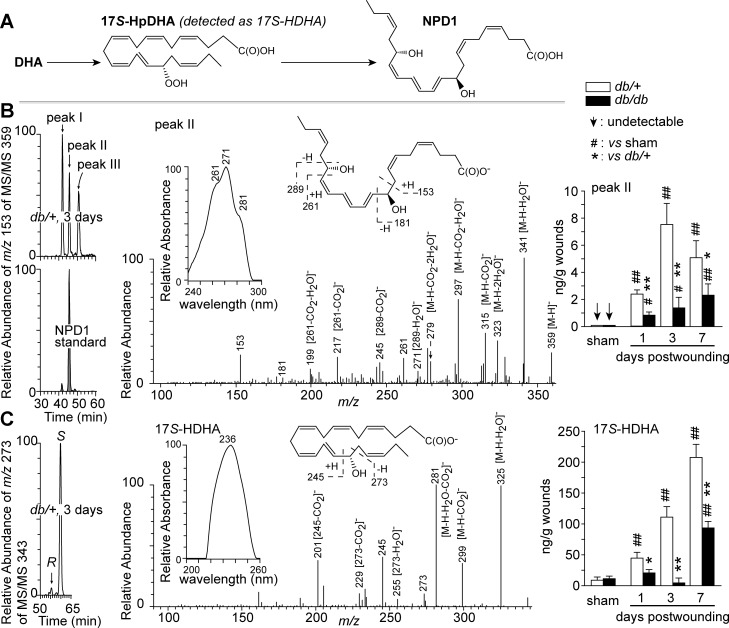
Fig. 1.
Diabetes altered endogenous NPD1 levels in wounds of diabetic db/db mice compared with non-diabetic db/+ mice. A: brief biosynthetic pathways for NPD1. B: NPD1. C: 17S-HDHA (a marker of NPD1 biosynthetic intermediate 17S-hydroperoxy DHA). Left: selective ion MS/MS aR chiral LC chromatograms. Middle: MS/MS spectra with insets of UV spectra and structure elucidation, which are representative for aR chiral LC-UV-MS/MS analysis, and acquired from wounds collected from db/+ mice at 3 days post-wounding (dpw). Right: quantitative kinetic levels of each compound in wounds. Sham mice underwent no wounding. Excisional wounds were collected at 1, 3, or 7 dpw after death, extracted and analyzed by chiral LC-UV-MS/MS. Data are means ± SE (n = 5). Significant difference vs. db/+: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Significant difference vs. sham: #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01; vs. sham.