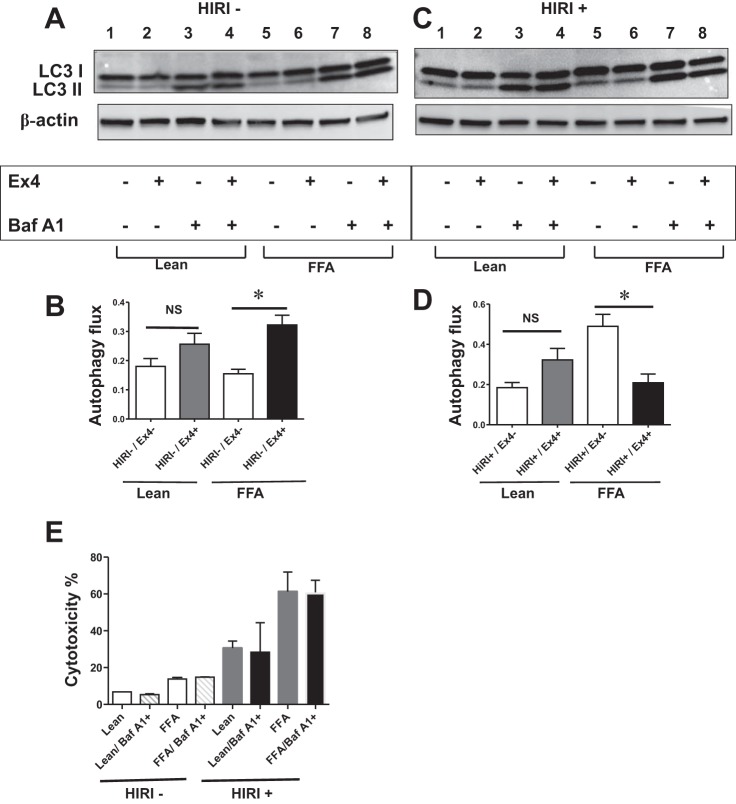
Fig. 6.
A and B: Ex4 increases autophagic flux in steatotic hepatocytes exposed to normoxia (HIRI−). Autophagic flux was assessed using BafA1 (10 nM). A: Western blot for LC3 I/II and β-actin (loading control). Lanes 1 and 5, Ex4−/BafA1−; lanes 2 and 6, Ex4+/BafA1−; lanes 3 and 7, Ex4−/BafA1+; lanes 4 and 8, Ex4+/BafA1+. Lanes 1–4 are from lean cells, and lanes 5–8 are from steatotic (FFA) cells. B: graphical representation of autophagic flux, which was calculated using equation in materials and methods. Values are means ± SD. FFA/Ex4− vs. FFA/Ex4+ (P < 0.03). C and D: Ex4 decreases autophagic flux in steatotic hepatocytes exposed to HIRI. C: Western blot for LC3 I/II and β-actin. Lanes 1 and 5, Ex4−/BafA1−; lanes 2 and 6, Ex4+/BafA1−; lanes 3 and 7, Ex4−/BafA1+; lanes 4 and 8: Ex4+/BafA1+. Lanes 1–4 are from lean cells, and lanes 5–8 are from steatotic (FFA) cells. Autophagic flux was assessed as described in materials and methods. D: graphical representation of autophagic flux. There was a significant decrease in autophagic flux in the Ex4-treated FFA cells: FFA/Ex4− vs. FFA/Ex4+ (P < 0.01). E: BafA1 at 10 nM, the concentration at which BafA1 inhibits autophagy flux, is not cytotoxic, nor does it confer survival advantage to lean and steatotic hepatocytes exposed to normoxia, as well as HIRI. Lean and steatotic HuH7 cells were treated with BafA1 (10 nM) during normoxia and HIRI, and LDH activity was measured to calculate percent cytotoxicity. Values are means ± SD of triplicate plates. *P < 0.05.