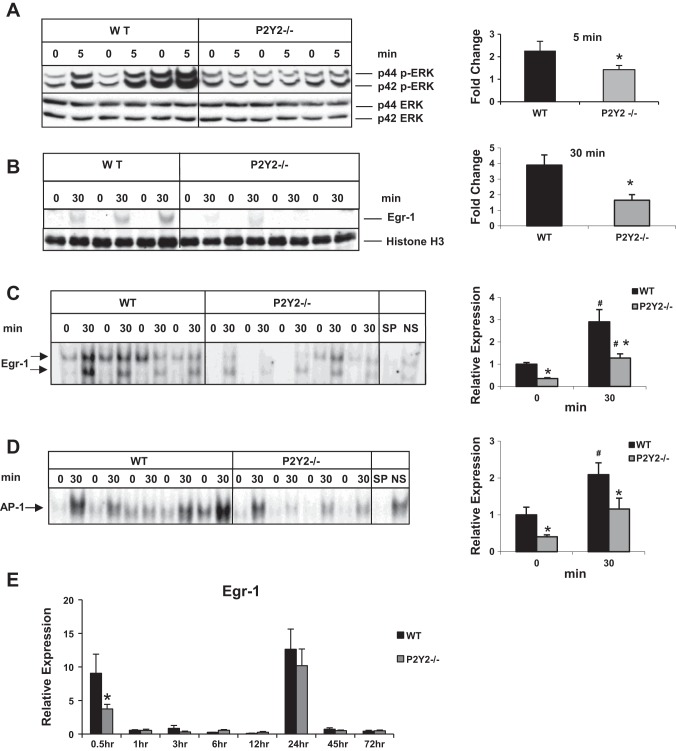
Fig. 3.
Early induction of p42/44 ERK MAPK and Egr-1 in response to PH is attenuated in P2Y2−/−. Western blotting for phospho-p42/44 ERK (Thr202/Tyr204) and total ERK of total proteins from (A) resected lobes (0 min) and remnant livers (5 min) of each animal; n = WT: 3, KO: 3; *P < 0.05 vs. WT. B: Western blotting for Egr-1 from nuclear protein extracts from the resected lobes (0 min) and remnant livers (30 min) of each animal; *P < 0.05 vs. WT; n = WT: 3, KO: 4. C: electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) for Egr-1 DNA-binding activity of nuclear protein extracts of the resected lobes (0 h) and remnant livers (30 min) of each animal; n = WT: 4, KO: 5. Arrows represent Egr-1-specific DNA binding activity. Specificity of binding was determined based on cold competition with 100-fold excess of specific and nonspecific oligonucleotides; *P < 0.05 vs. WT, #P < 0.05 (0 vs. 30 min). Protein loading control: histone H3 (nuclear). Data represent means ± SE. D: nuclear proteins isolated from the resected lobes (0 h) and remnant livers (30 min) of each animal were analyzed by EMSA for DNA-binding activity with radiolabeled double-stranded oligonucleotides containing AP-1 consensus binding sites. Specificity of AP-1 DNA-binding activity was determined by cold competition assay with 100-fold excess of cold specific and nonspecific oligonucleotides in the incubation mixture; n = WT: 5, KO: 4. E: total RNA isolated from the resected lobes and remnant livers harvested at 0.5–72 h of the WT and P2Y2−/− livers were analyzed by qRT-PCR for Egr-1 mRNA expression. Fold change is calculated with reference to the expression in the respective resected lobes for each time point tested. Data represent means ± SE; n = WT: 9, KO: 10 (0.5 h); WT: 4, KO: 4 (1 h); WT: 4, KO: 4 (3 h); WT: 4, KO: 4 (6 h); WT: 4, KO: 4 (12 h), WT: 12, KO: 11 (24 h); WT: 4, KO: 4 (45 h); WT: 4, KO: 4 (72 h). *P < 0.05 vs. WT, #P < 0.05 vs. WT Control (0 h).