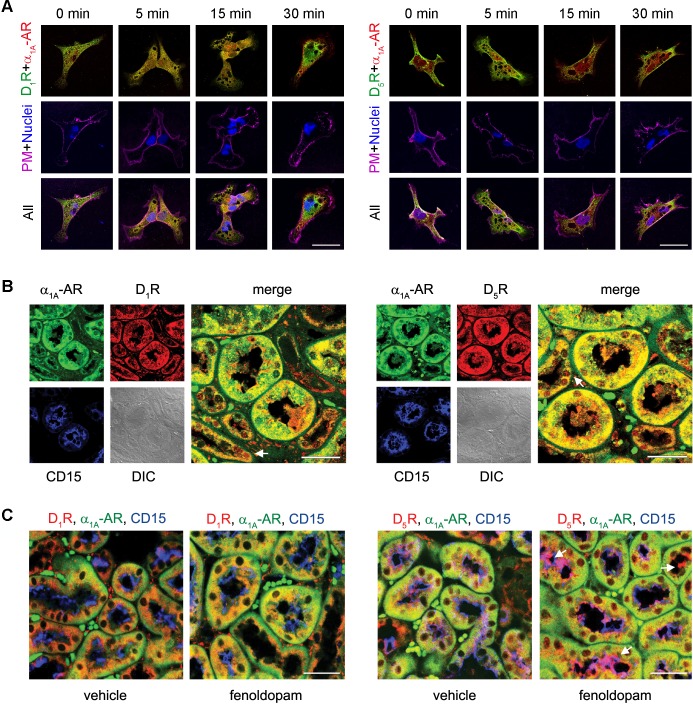
Fig. 2.
Colocalization of D1-like dopamine receptors and α1A-ARs in hRPTCs and human and mouse kidneys. A: hRPTCs were grown on coverslips, serum starved for 1 h, and treated with Fen (1 μM) at the indicated time points. Cells were then fixed, double immunostained for D1Rs or D5Rs (pseudocolored green) and α1A-ARs (pseudocolored red), and visualized via confocal microscopy. Around 30–40 cells were scored, and 5–10 cells were imaged per experiment. The lipid rafts of the plasma membrane were visualized using cholera toxin subunit B (CTxB) conjugated with Alexa fluor 647, and nuclei were visualized using 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Colocalization between D1-like dopamine receptors and α1A-ARs is denoted by yellow punctate areas, whereas colocalization of these receptors with the plasma membrane (PM) is denoted by white in the merged images. B: human kidney sections were antigen retrieved and double immunostained for D1Rs or D5Rs (pseudocolored red) and α1A-ARs (pseudocolored green). Proximal tubules were visualized using brush border-localized CD15 (pseudocolored blue) as a marker. Distal convoluted tubules are indicated with white arrows. DIC, differential interference contrast. C: C57Bl/6J mice were treated with Fen (2 μg·kg−1·min−1 iv) or Veh for 30 min, and kidneys were collected and prepared for immunofluorescence to evaluate the distribution and colocalization of D1Rs or D5Rs (pseudocolored red) and α1A-ARs (pseudocolored green). Proximal tubules were visualized using CD15 (pseudocolored blue) as a marker. The localization of D5Rs at the brush border is indicated by the white arrows. Magnification: ×600. Scale bars = 10 μm. n = 3.