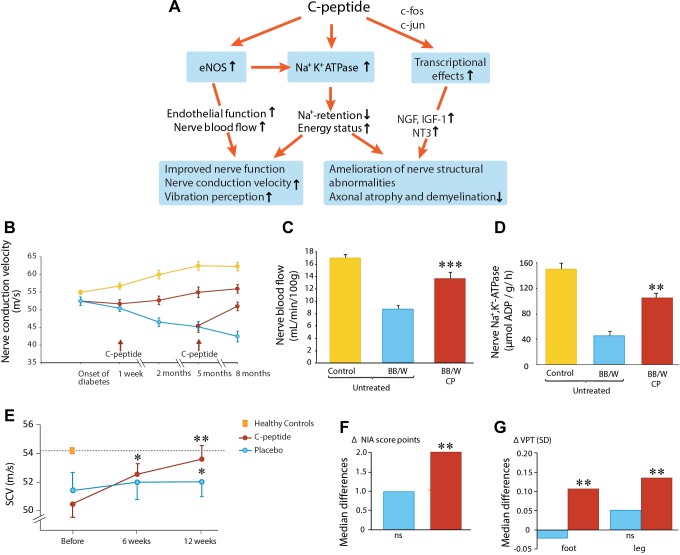
Fig. 1.
C-peptide and diabetic neuropathy. A: schematic overview of C-peptide's effects on nerve function and structure in diabetes. eNOS, endothelial NO synthase. B: effects of C-peptide (red) or placebo (blue) administration for up to 8 mo on nerve conduction velocity (NCV) in diabetic rats. Yellow symbols indicate NCV development in healthy nondiabetic animals; data from Ref. 97. C: sciatic nerve blood flow in healty (yellow), untreated diabetic (blue), and C-peptide-treated (red) diabetic BB/W rats; data from Ref. 15. D: Na+,K+-ATPase activity of the sciatic nerve in healthy (yellow), untreated diabetic (blue), and C-peptide-treated diabetic rats; data from Ref. 97. E: effects of C-peptide in replacement dose (red) or placebo (blue) for 3 mo on sensory nerve conduction velocity (SCV) in type 1 diabetes subjects with early-stage nerve impairment (Ref. 19). F: influence of C-peptide (red) or placebo (blue) administration for 6 mo on neuropathy impairment score (NIA) (Ref. 20). G: vibration perception in subjects with type 1 diabetes and manifest neuropathy; data from Ref. 20.