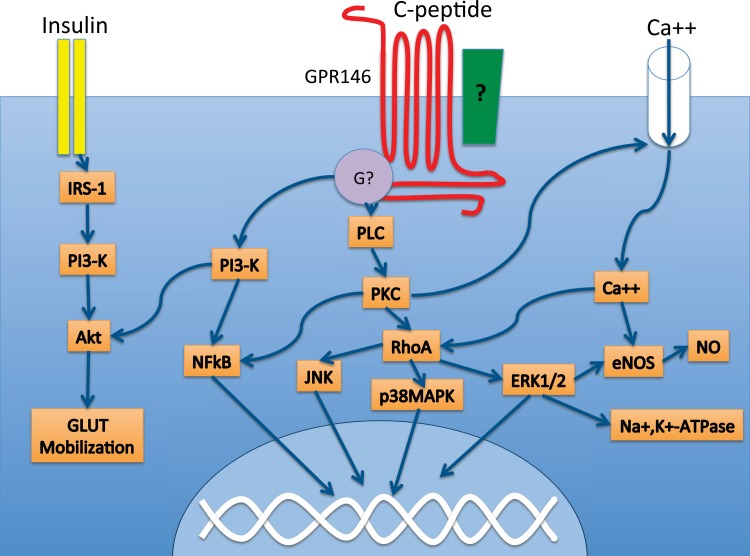
Fig. 4.
C-peptide-initiated signaling cascades. C-peptide is associated with the regulation of several signaling cascades, including phospholipase C (PLC) and the NF-κB pathway. These intracellular signaling events are likely mediated by a G protein-coupled receptor such as GPR146, which has been shown to be necessary for C-peptide signaling in KATOIII cells. GPR146 interacts with an as yet unknown G protein, which could be either Gαi or Gαo, since several of the cellular actions of C-peptide were shown to be pertussis toxin sensitive. GPR146 may interact physically with additional proteins on the cell membrane, such as an integrin (green box). C-peptide and insulin appear to functionally interact, particularly at the level of Akt. Akt, protein kinase B; Ca++, calcium ion; eNOS, endothelial NO synthase; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; G?, G protein; GLUT, glucose transporter; IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate 1; JNK, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; Na+,K+-ATPase, sodium/potassium ATPase; NO, nitric oxide; NF-κB, nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PKC, protein kinase C; PLC, phospholipase C; PI3-K, phosphotidylinositol 3-kinase; p38 MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; RhoA, Ras homolog gene family, member A.