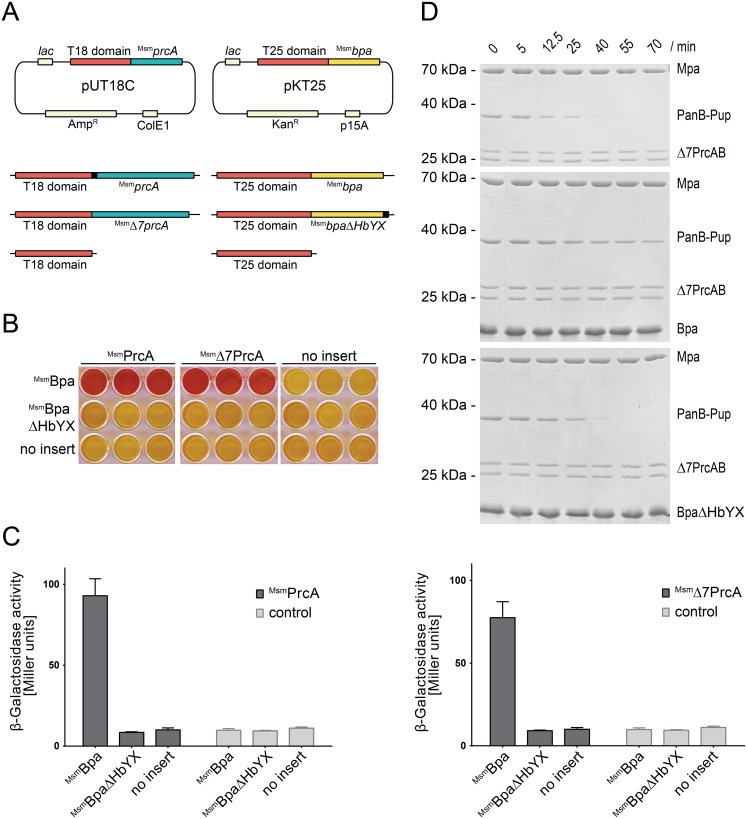
Figure 2. Bpa interacts with the 20S proteasome through its C-terminal HbYX motif.
A, Vector constructs for the bacterial two-hybrid screen. PrcA and Δ7PrcA were fused to the C-terminus of the catalytic T18 domain, Bpa and BpaΔHbYX to the C-terminus of the catalytic T25 domain of adenylate cyclase. B, MacConkey agar matrix of all pairwise combinations of the pUT18C and pKT25 constructs in triplicates. Successful interaction between T18 and T25 switches the colony from lac− to lac+ and the resulting acidification of the agar is visualized by the pH indicator turning red. C, A quantitative β-galactosidase assay of the same hybrid experiments as shown in B. The assay was performed on chloroform-treated E. coli cells grown overnight in liquid LB medium containing 0.5 mM IPTG. The background activity is indicated by the negative control (no insert, corresponding to pKT25 and pUT18C carrying only the adenylate cyclase domains without fusion). Bars represent averages ± SEM of at least three replicates. D, Mpa-mediated proteasomal PanB-Pup degradation is inhibited in presence of association-competent Bpa but not in presence of BpaΔHbYX. Concentrations: Mpa (0.2 µM), 20S proteasome (0.1 µM), Bpa or BpaΔHbYX (14 µM protomer).