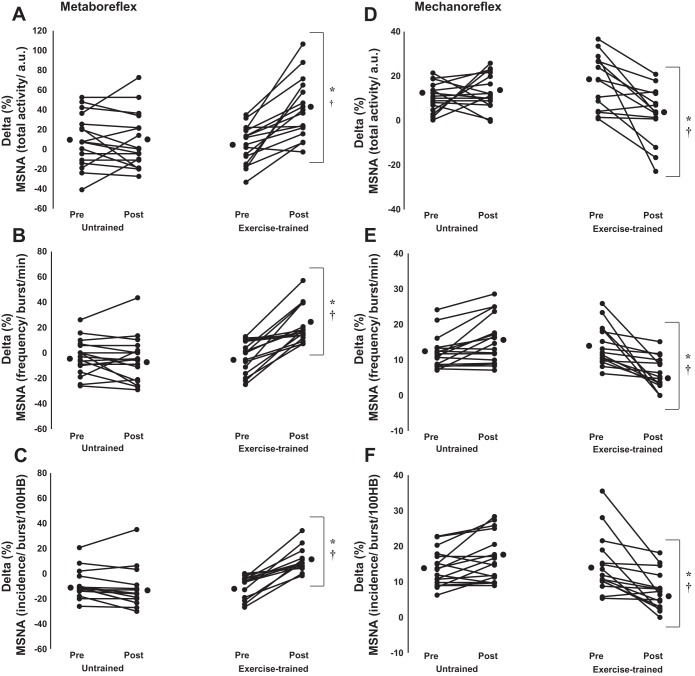
Fig. 4.
Metaboreflex control of MSNA assessed by %changes between the 1st minute of postexercise regional circulatory arrest and rest period in untrained (n = 17) and exercise-trained (n = 16) heart failure patients. A: delta changes in MSNA total activity (a.u.). B: frequency (bursts/min). C: incidence (bursts/100 HB). Mechanoreflex control of MSNA assessed by difference between the peak of passive exercise and rest period in untrained (n = 17) and exercise-trained (n = 16) heart failure patients. D: delta changes in MSNA total activity (a.u.). E: frequency (bursts/min). F: incidence (bursts/100 HB). Exercise training markedly increased the MSNA responses during metaboreceptors stimulation in heart failure patients. In contrast, exercise training significantly decreased MSNA responses during mechanoreceptors stimulation. Values are mean individual response. *P < 0.05 vs. pre within group. †P < 0.05 vs. untrained.