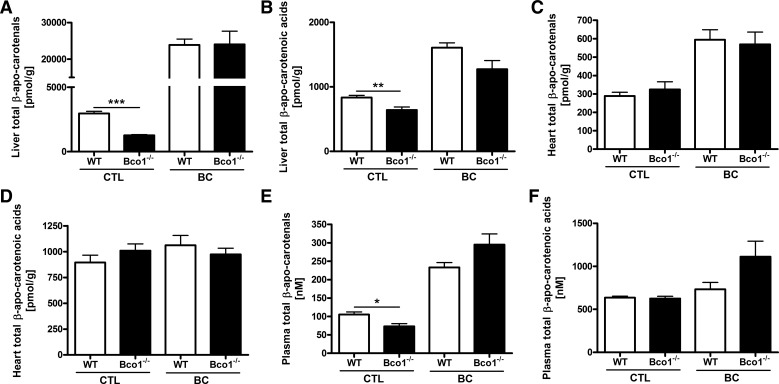
Fig. 2.
Effects of Bco1 deficiency and β-carotene supplementation on total β-apo-carotenal and total β-apo-carotenoic acid levels in the liver, heart, and plasma. The total β-apo-carotenal level was the sum of β-apo-14′-, β-apo-12′-, β-apo-10′-, and β-apo-8′-carotenal levels determined individually for each tissue. The total β-apo-carotenoic acid level was the sum of β-apo-14′-, β-apo-12′-, β-apo-10′-, and β-apo-8′-carotenoic acid levels determined individually for each tissue. Liver total β-apo-carotenal (A) and total β-apo-carotenoic acid (B) levels were statistically different for chow-fed [control (CTL)] WT and Bco1−/− mice but not for mice that received a 1-mg dose of β-carotene (BC) 3 days before euthanization. Heart total β-apo-carotenal (C) and total β-apo-carotenoic acid (D) levels were not different for WT or Bco1−/− mice that received either a chow diet (CTL) or were supplemented with a 1-mg dose of β-carotene (BC) 3 days before euthanization. Plasma levels of total β-apo-carotenals (E) but not total β-apo-carotenoic acids (F) were statistically different in Bco1−/− mice compared WT mice maintained on a chow diet (CTL). Administration of a 1-mg dose of β-carotene (BC) 3 days before euthanization abolished the effect of genotype on plasma total β-apo-carotenal levels (E). Values are means ± SE; n = 5–8. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.