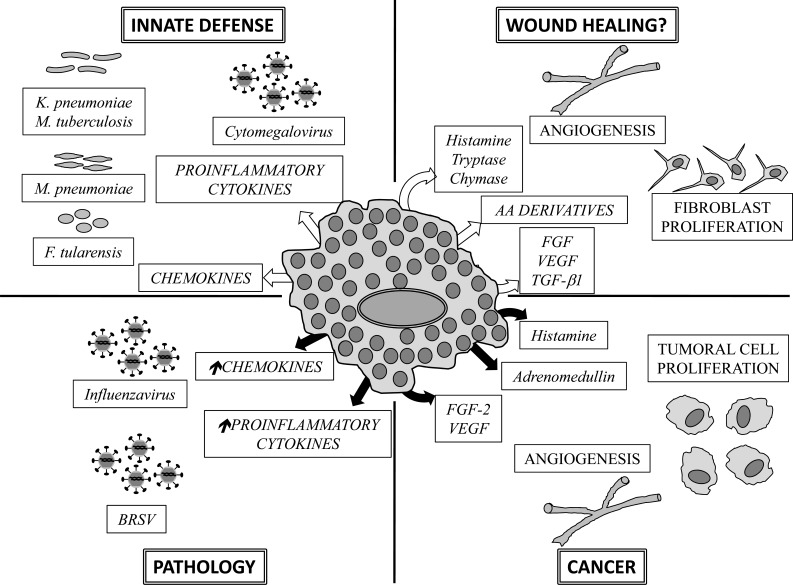
Fig. (2).
Functions of mast cells in the lungs. The dual role of mast cells in lung functions is depicted. White arrows indicate release of mediators that contribute to lung homeostasis. Black arrows designate liberation of mediators that contribute to pathological states in the lungs. Some mediators participate in lung homeostasis or contribute to pathology, depending on their concentration or on the timing of their production. AA: Arachidonic acid, FGF: Fibroblast Growth Factor, VEGF: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor, TGF-β1: Transforming Growth Factor β1, BRSV: Bovine Respiratory Syncitial Virus. Arrows pointing up indicate exacerbated production.