Table 1.
Corrector activity, Vmax, and cLogP data for bisazoles.
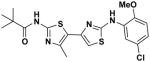 1 1
|
EC50(μM)a = 0.87 Vmax(μM/s)b = 97.97 CLogP = 5.60 |
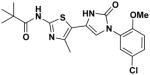 2a′ 2a′
|
EC50(μM)a = not active Vmax(μM/s)b = not active CLogP = 3.95 |
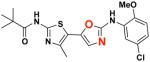 2b 2b
|
EC50(μM)a = 0.74 Vmax(μM/s)b = 84.46 CLogP = 5.20 |
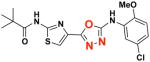 2c 2c
|
EC50(μM)a = 0.66 Vmax(μM/s)b = 65.00 CLogP = 4.39 |
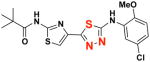 2d 2d
|
EC50(μM)a = not active Vmax(μM/s)b = not active CLogP = 5.04 |
 2e 2e
|
EC50(μM)a = 0.59 Vmax(μM/s)b = 35.46 CLogP = 4.39 |
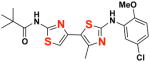 23 23
|
EC50(μM)a = not active Vmax(μM/s)b = not active CLogP = 5.60 |
Concentration where the increased I− influx is 50% of Vmax.
Vmax is the maximum increase in I− influx due to compound dosing.
