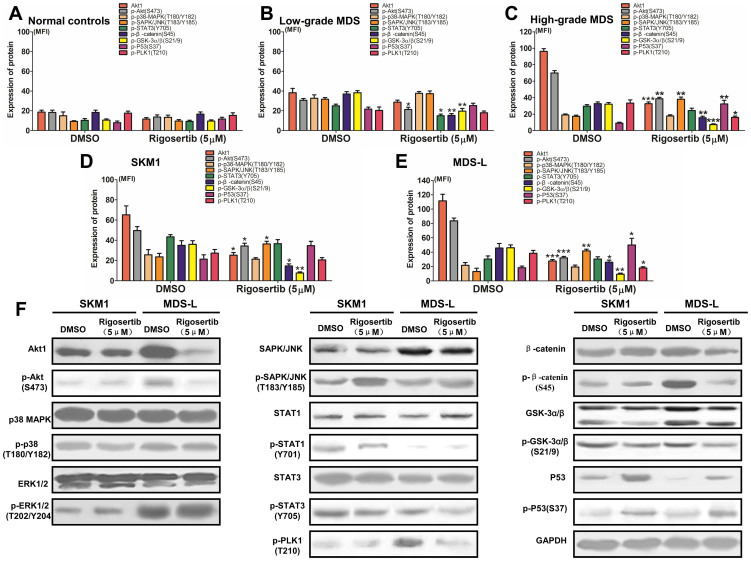
Figure 5. Rigosertib could modify multiple signaling pathways in MDS and MDS cell lines.
(A) Rigosertib did not affect the expression and phosphorylation levels of signaling transducers, including Akt, p38, SAPK/JNK, STAT3, β-catenin, GSK3α/β and P53, in normal CD34+ cells because it did not activate these proteins; (B) In patients with low-grade MDS, rigosertib administration could somewhat reduce the phosphorylation of Akt, β-catenin and GSK3α/β; (C) In patients with high-grade MDS, rigosertib markedly reduced the phosphorylation of Akt, β-catenin and GSK3α/β, while the phosphorylation of SAPK/JNK and P53 was enhanced; In the SKM1 (D) and MDS-L (E) cell lines, the same results could be observed as in patients with high-grade MDS. (F) Western blot was performed to validate the results acquired from FCM in the MDS-L and SKM1 cell lines. Representative graphic from three experiments was shown. For each patient or cell line, experiments were carried out three times. Error bars throughout represent the SEM. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001 (two-tailed, student T test).