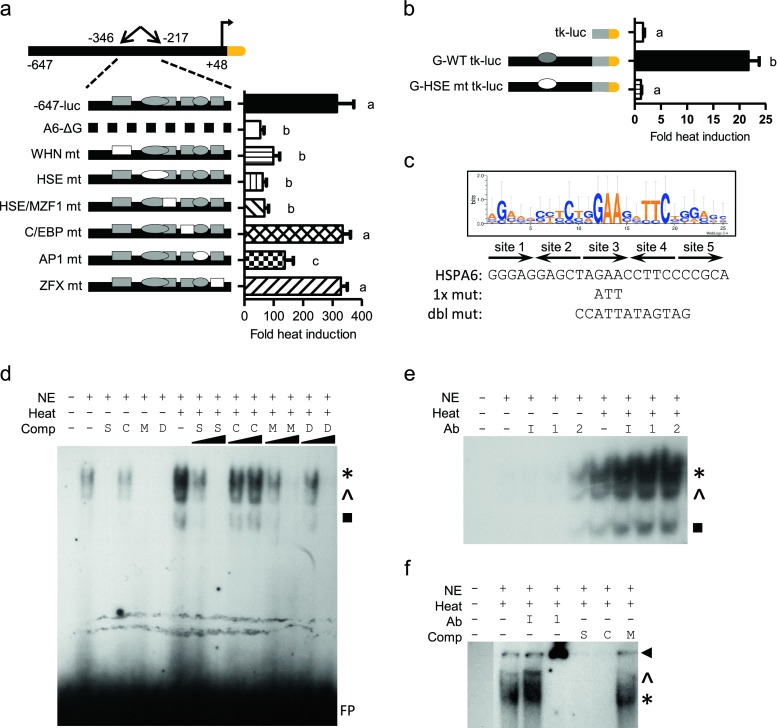
Fig. 6.
Characterization of the −284 bp HSE in HaCaT cells. Site-specific mutations within the −647-luc construct (a) or fragment G-tk-luc construct (b). Filled shapes indicate wild-type elements. Specific site mutants are shown as empty shapes. Graphs shown as fold heat induction. Statistically significant values are indicated by different letters using a p value <0.05 as determined using ANOVA with Newman Keuls post hoc. Bars are mean + SEM from three experimental repeats, each bar from triplicate cultures. c Sequence alignment of functional 5× inverted HSE repeats from several human HSP promoters shown as a WebLogo graphical representation. Letter height reflects occurrence of the nucleotide. Below graphic are the predicted HSPA6 − 284 bp HSE, the single and double mutant sequences. Arrows indicate single HSE repeat. EMSA of HSPA6 HSE incubated with unlabeled competitor oligomers (d) or with antibodies (e). EMSA of consensus HSE (f). Nonradiolabeled competitor oligomers include self HSPA6 HSE site (S), consensus HSE (C), mutated HSE (M), or double mutated HSE (D) at 10- or 100-fold excess. Antibodies include nonspecific IgG (I), anti-HSF1 (1), or anti-HSF2 (2). Asterisks denote major binding species, while caret and black box denote minor binding species. FP denotes free probe. Arrowheads denote supershift