Fig. 1. Air-liquid interface culture of airway epithelial cells.
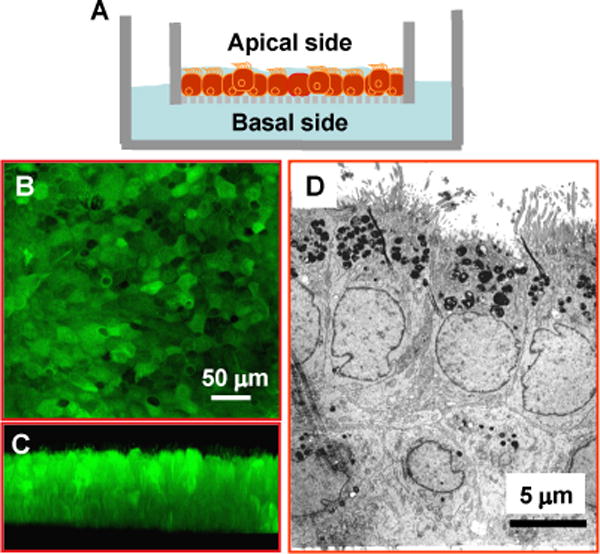
A) A drawing depicting the air-liquid interface culture. NHBE cells are seeded on a semi-permeable filter and grown at the air-liquid interface. Nutritional support comes from the basolateral side and the apical side is exposed to the air. Such a setting facilitates epithelial polarization and differentiation. B & C) Confocal micrographs demonstrate that the cultured airway epithelia form a tight epithelial sheet as seen under horizontal optical scanning with apical ciliation discernable by vertical scanning. D) The electron micrograph shows the typical characteristics of polarized epithelium with apical cilia and microvilli, and pseudopodia extending into the basal filter membrane.
