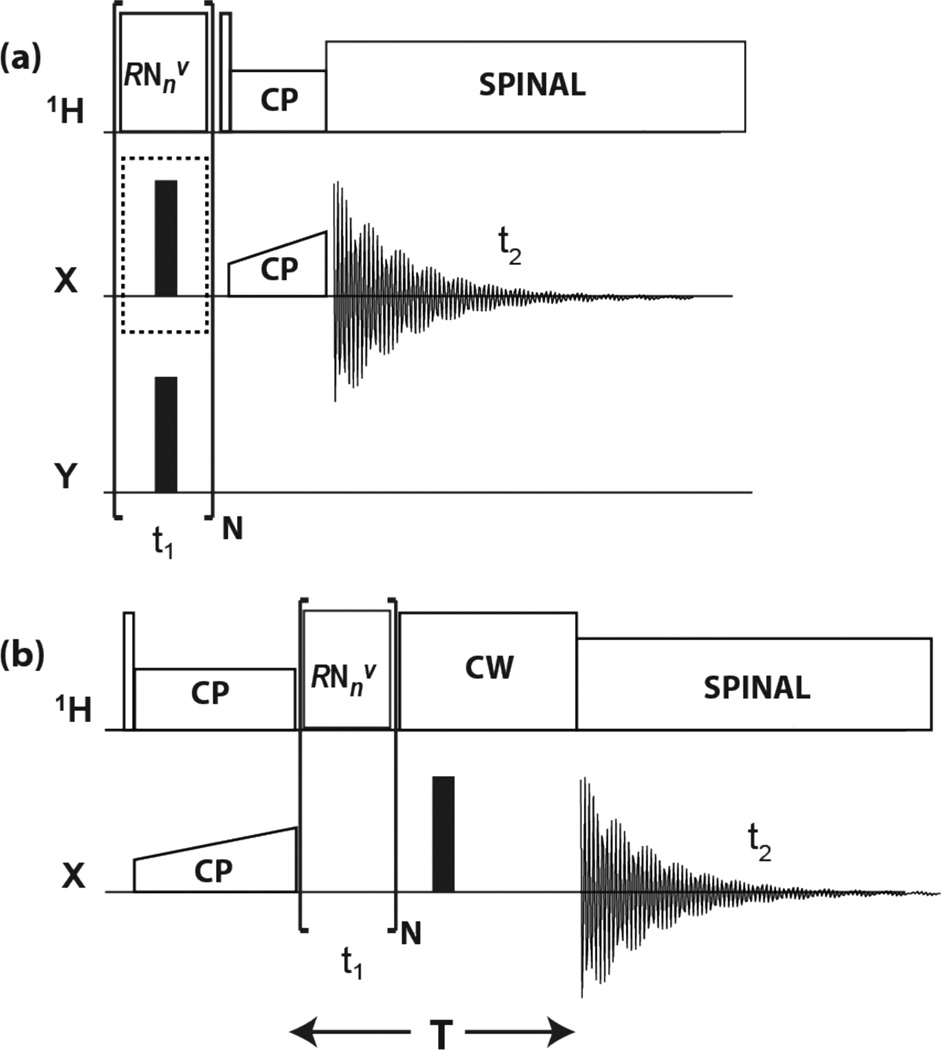
Figure 1.
Pulse sequences for (a) RN-1H(Xund) and RN-1H(Xdec), and (b) RN-X 2D experiments. In the present applications, X and Y represent 15N and 13C, or 13C and 15N, respectively. Rotor synchronized RNnv symmetry rf pulses are applied during t1 evolution time to reintroduce 1H CSA and 1H−X dipolar interactions under MAS conditions. Empty and solid rectangles denote π/2 and π pulses, respectively. In (a), the time dependence of 1H z-magnetization is monitored, either with application of the X decoupling π pulses for RN-1H(Xdec), or without for RN-1H(Xund). This optional decoupling pulse is marked by a dotted-line enclosure. Y is decoupled by π pulses during t1. Site-selective 1H detection is accomplished by short-contact-time CP to X. In (b), the time evolution of X x-magnetization is monitored with refocusing of the chemical shift over a constant evolution period T.