Figure 2.
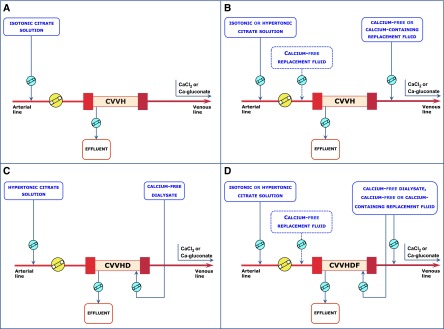
Schematic representation of RCA for the different continuous RRT modalities. In protocols adopting high-concentration citrate solutions, the use of a low-sodium dialysate and/or replacement fluid is generally required to prevent hypernatremia. In protocols adopting low-concentration citrate solutions, citrate acts as both an anticoagulant and a predilution replacement fluid, thus contributing to the total continuous RRT dose. Sections A and C display RCA circuits in predilution-only CVVH and CVVHD modalities, respectively. The dotted boxes in B and D indicate the possibility of using a calcium-free predilution replacement fluid along with a separate hypertonic citrate solution to obtain predilution and postdilution CVVH or CVVHDF.
