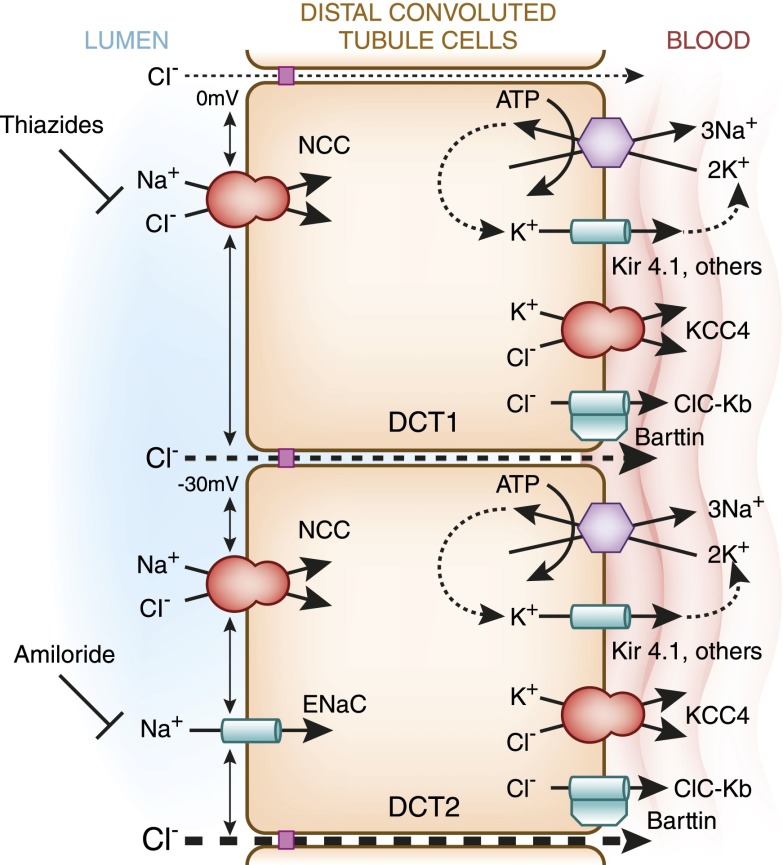
Figure 2.
A model of NaCl reabsorption by cells of the early and late DCTs. Note that the transepithelial voltage is close to zero in the DCT1 and becomes progressively negative in the DCT2. In the early DCT, apical sodium reabsorption is exclusively mediated by thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter (NCC), whereas in the late DCT, both NCC and amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channels (ENaCs) are present. The electrogenic transport of sodium by ENaC contributes to the lumen-negative transepithelial voltage. Basolateral sodium efflux is mediated by the Na+-K+-ATPase and aided by Kir4.1-mediated potassium leak currents. Chloride transport is carried out by the chloride channel ClC-Kb and potassium chloride cotransporter 4 (KCC4; SLC12A7).