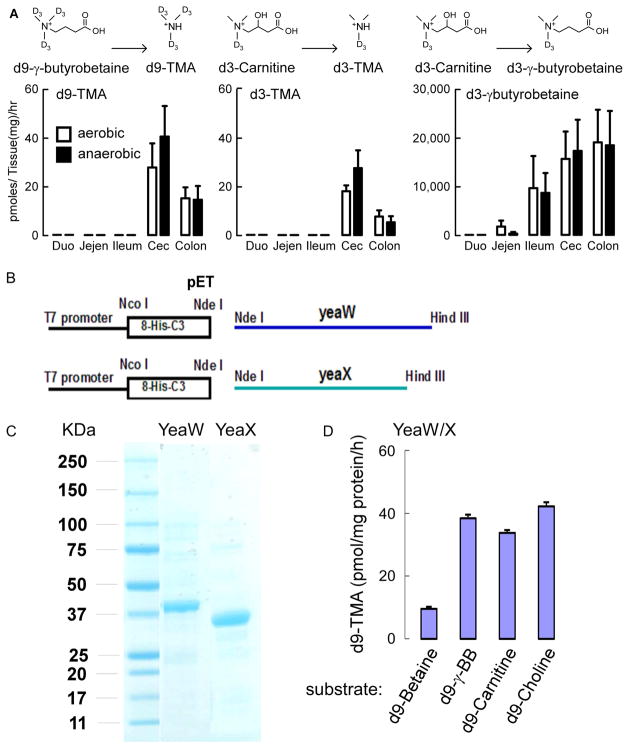
Figure 3. Gut microbes convert L-carnitine into γBB anatomically proximal to TMA, and the microbial enzyme yeaW/X shows TMA lyase activity with multiple trimethylamine nutrients.
(A) C57BL/6J Female mouse intestines (n=7) were sectioned into two complementary pieces for incubation at 37 °C for 18 hours with equimolar amounts of d3-L-carnitine (middle and right panels) or d9-γBB (left panel) under either aerobic (open bars) or anaerobic(closed bars)conditions, as indicated. Deuterated trimethylamine analytes were quantified by stable isotope dilution LC/MS/MS as described in Experimental Procedures. d3-γBB production from d3-L-carnitine is approximately 1,000-fold higher (lower panel) than d3-TMA production (middle panel). Duo =Duodenum, Jejen=Jejenum, Cec=Cecum (B) Cloning of YeaW/YeaX from E. coli DH10b into pET at NdeI and HindIII sites and transforming E. coli BL21. (C) SDS-PAGE confirmation of the purified yeaW and yeaX from E. coli BL21 lysate transformed with pET-yeaW and pET-yeaX, respectively. Both yeaW and yeaX contain 8xHis Tag. (D) YeaW/X catalyzes production of TMA from multiple TMA containing compounds. Data presented are mean ± SE for triplicate determinations from 2 independent replicates of purified proteins. (see also Figure S3–S7).