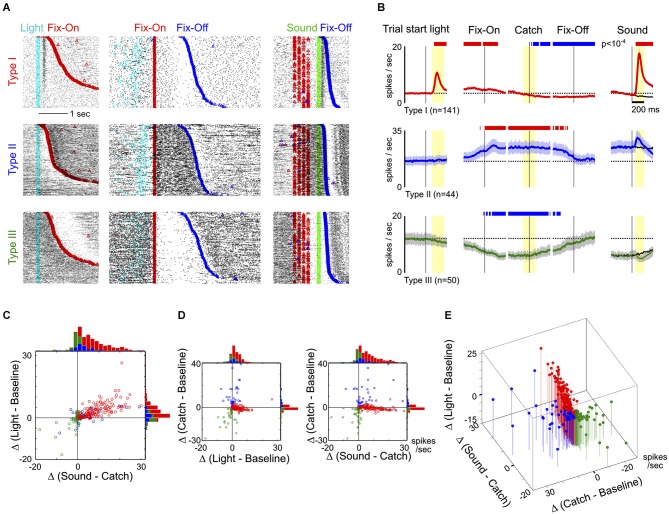
Figure 2.
Response features of the three main types of neurons in the BF region. (A) Raster plots of activity from three example neurons, one in each row, from the three types of BF neurons. Individual trials were aligned to trial-start light signal and sorted by the latency to enter fixation port (Fix-On; left column), or aligned to Fix-On in Catch trials and sorted by the latency to exit fixation port (Fix-Off; middle column), or aligned to sound onset and sorted by reaction time (right column). (B) Average PSTHs (± s.e.m.) for the three types of BF neurons in response to different trial events, indicated by the black vertical line. The left column shows responses to the trial-start light signal. The middle three columns show responses to three events in Catch trials: Fix-On, the Catch stimulus (Catch) and Fix-Off. The right column shows responses to sound stimuli, with responses to the Catch stimulus shown in black for comparison. Dashed lines depict the average baseline firing rates for each type of neuron. Significant changes in firing rates are indicated by red (increased rate) and blue (decreased rate) bars. In the left four columns, firing rates are relative to baseline firing rates; in the right column, they are relative to catch trials (paired t-tests, p < 10−4). (C) Scatter plot of individual neuronal response amplitudes to the trial start light (relative to baseline) vs. sounds (relative to catch stimulus), along with marginal distributions. The time windows for response amplitude calculation are indicated by yellow shaded areas in (B). There was substantial overlap between Type-I and II neurons. (D) Scatter plots of individual neuronal response amplitudes between light vs. catch stimulus and sound vs. catch stimulus. Conventions are the same as in (C). (E) The three features combined separates the three main types of BF neurons.