Figure 7.
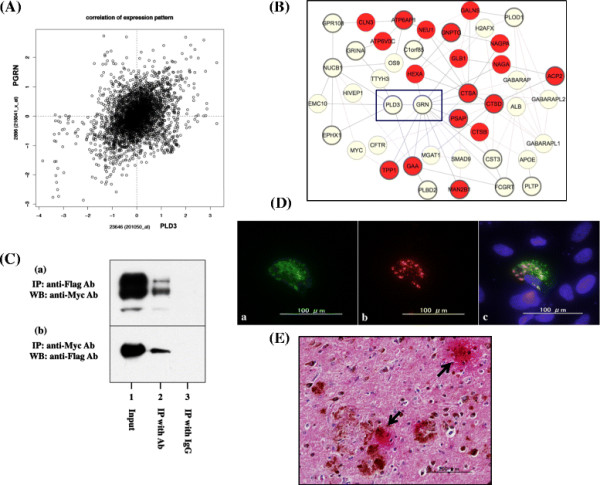
Coexpression and molecular interaction of PLD3 with progranulin. (A), (B) Coexpression of PLD3 and progranulin (PGRN). The genes coexpressed with PLD3 were identified by database search on COXPRESdb [23] and are listed in Additional file 6. (A) Correlation coefficient of gene expression between PLD3 (x axis indicates probe ID 201050_at) and PRGN (y axis indicates probe ID 216041_x_at) is 0.454. (B) Interactive network of the set of genes coexpressed with PLD3 shows an enrichment of lysosomal proteins (nodes indicated in red). The interaction between PLD3 and GRN is highlighted by a blue square. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of PLD3 and PGRN. Myc-tagged PLD3 and Flag-tagged PGRN were coexpressed in HEK293 cells. The protein extract was processed for (a) immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-Flag antibody followed by western blot (WB) with anti-Myc antibody or (b) IP with anti-Myc antibody followed by WB with anti-Flag antibody. Lane 1, input control; lane 2, IP with the specific antibody; lane 3, IP with normal IgG. (D) Colocalization of PLD3 and PGRN in cultured cells. ZsGreen-tagged PLD3 and DsRed-tagged PGRN were coexpressed in SK-N-SH cells. (a) PLD3, (b) PGRN, and (c) merge. (E) Colocalization of PLD3 and PGRN in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) brains. The coexpression of PLD3 (brown) and PGRN (red) was studied in the frontal cortex of AD brains by double-labeling immunohistochemistry. Arrows indicate the prominent accumulation of PLD3 and PGRN on neuritic plaques. Ab, antibody; PLD, phospholipase D.
