FIGURE 1.
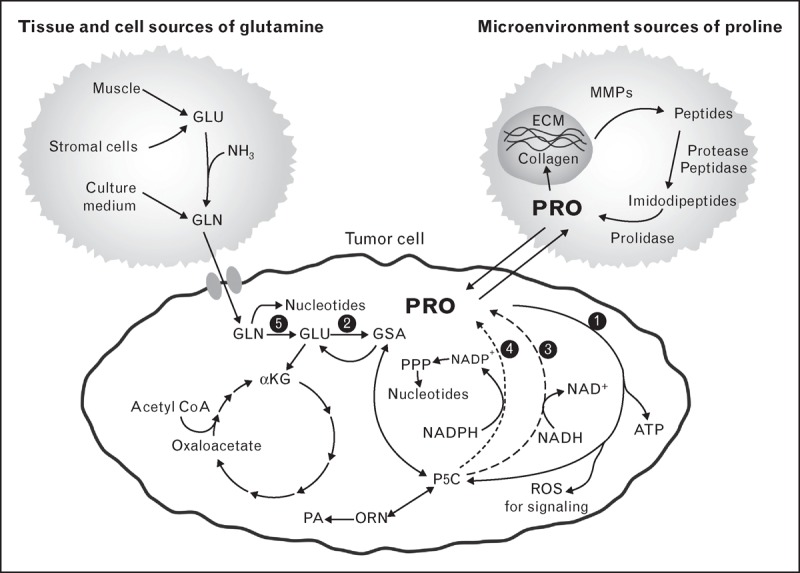
A proposed metabolic model involving glutamine, proline and collagen. The depicted tumor cell is also applicable to nonmalignant proliferating cells. The sources for glutamine are shown on the upper left and the source for proline is shown in the upper right. These are not necessarily specific for cellular or other anatomic sites. GSA and P5C are tautomers. Their interconversions are spontaneous. Overall, the proposed pathway is that glutamine synthesized from adequate protein intake is used for energy and de-novo synthesis of purines and pyrimidines. Proline is an important amino acid product that is used for signaling as well as an alternate source of ATP. During nutritional plenty, proline is stored in collagen, the main component of ECM. This reservoir of proline can be mobilized during conditions of nutritional stress. ECM, extracellular matrix; GSA, glutamic-γ- semialdehyde; P5C, pyrroline-5-carboxylate; ORN, ornithine; PA, polyamines; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway. The black circles designate specific enzymes numbered as follows: 1, proline dehydrogenase a.k.a. proline oxidise; 2, P5C synthase; 3, P5C reductase 1 and 2; 4, P5C reductase L; 5, glutaminase.
